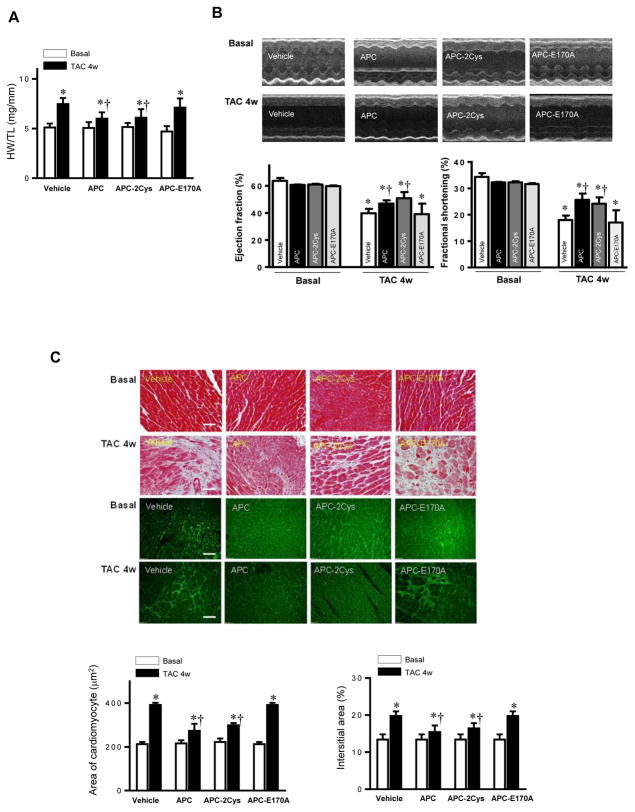
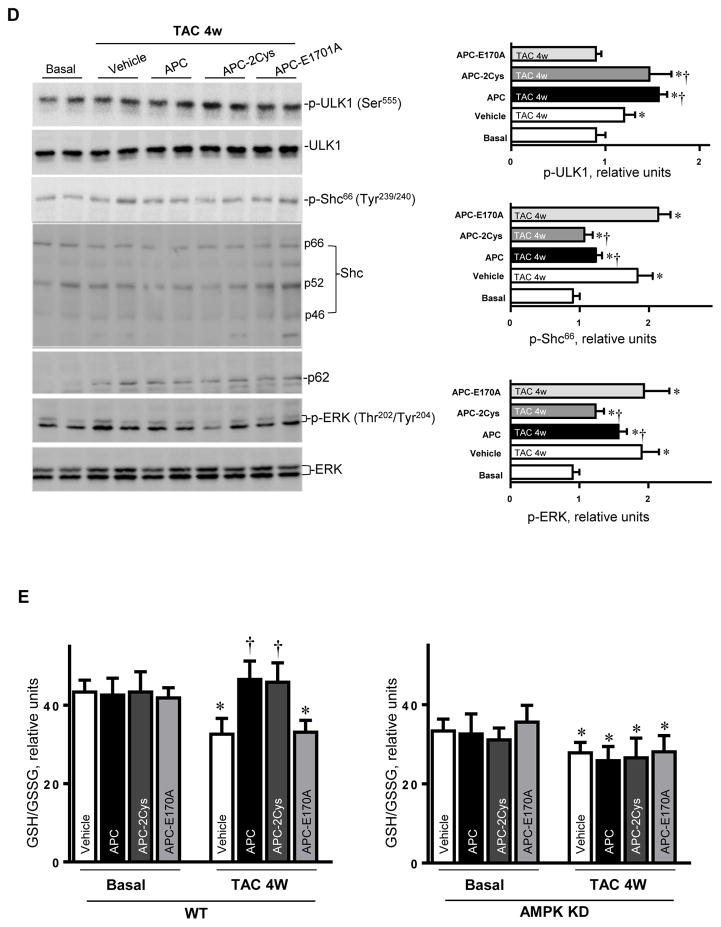
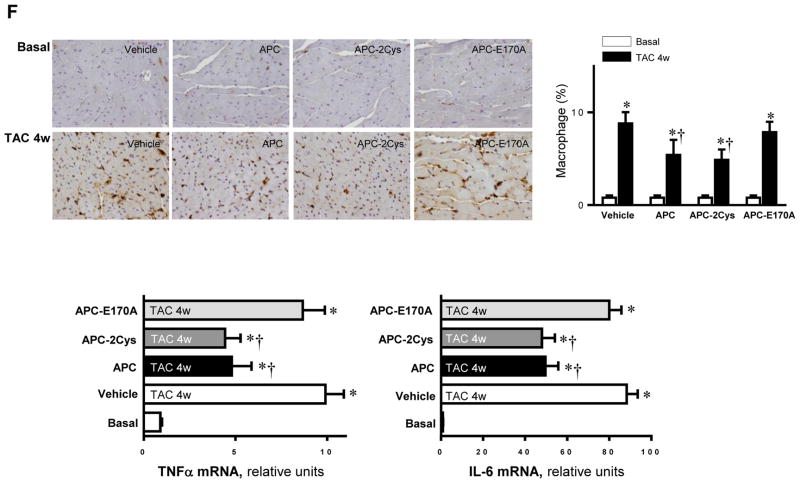
Figure 4.
Activated protein C (APC) derivatives ameliorate heart dysfunction mediated by pressure overload. (A) The left tibia length of WT mice with or without APC derivatives treatment under basal and 4 weeks of TAC conditions. Values are means ± SE, n=4–5 per group, *p<0.05 vs. corresponding Basal, †p<0.05 vs. Vehicle TAC. (B) Echocardiography showed the beneficial effects of APC derivatives on cardiac functions under basal and TAC-induced pressure overload conditions. Values are means ± SE, n=4 per group, *p<0.05 vs. Basal; †p<0.05 vs. Vehicle TAC. (C) The Masson trichrome and WGA staining to demonstrate the effects of APC derivatives on the fibrosis and hypertrophy caused by TAC-induced pressure overload. Values are means ± SE, n=4–5 per group, *p<0.05 vs. corresponding Basal, †p<0.05 vs. Vehicle TAC. (D) Immunoblotting showed the modulating effects of APC derivatives on autophagy, ULK1 signaling and p62 expression level, oxidative stress Shc and ERK signaling pathways in response to TAC-induced pressure overload. Value are means ± SE, n=5–6 per group, *p<0.05 vs. Basal; †p<0.05 vs. Vehicle TAC. (E) The ratio GSH/GSSG showed effects of APC derivatives on the intracellular redox status of hearts in response to TAC-induced pressure overload. Values are means ± SE, n=4–6 per group, *p<0.05 vs. corresponding Basal; †p<0.05 vs. Vehicle TAC. (F) Immunohistochemistry with Mac-2 antibody to show the macrophage infiltration under basal and TAC-induced pressure overload conditions. Lower panel: The real-time RT-PCR demonstrated that APC derivatives attenuate mRNA levels of TNFα and IL-6 proinflammatory cytokines caused by TAC-induced pressure overload. Values are means ± SE, n=3–6 per group, *p<0.05 vs. Basal; †p<0.05 vs. Vehicle TAC.