Figure 1.
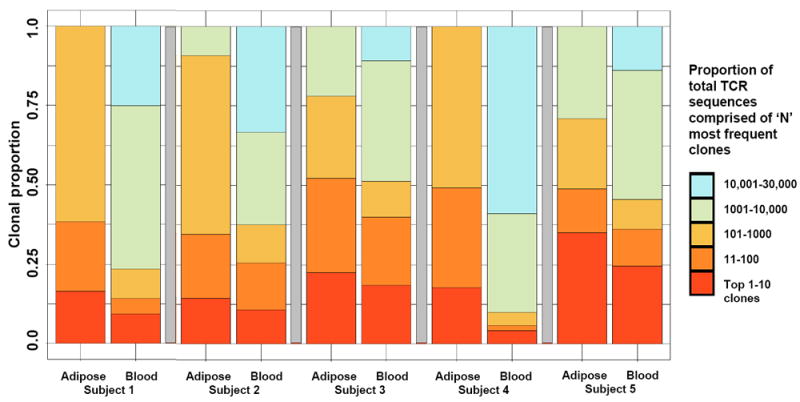
Greater clonality of the CD8+ T cell receptor β repertoire in adipose tissue compared to blood
Colored bars represent the relative proportion of all productive CD8+ T cell receptor (TCR)β sequences from each subject’s paired adipose tissue and blood that comprised the 10 most prevalent clones (red bar), the 100 most prevalent clones (dark orange bar), etc. Proportional downsampling and bootstrapping were used to account for read count distribution differences between tissue compartments. The 10 most prevalent TCRβ clones comprised a larger percentage of total clones in adipose tissue compared to paired blood in all 5 subjects (25% vs. 16% of total repertoire, respectively; P=0.04), and the Shannon’s Entropy index, a measure of overall repertoire diversity, was lower in adipose tissue compared to blood (4.39 vs. 4.46, respectively; P=0.05).
