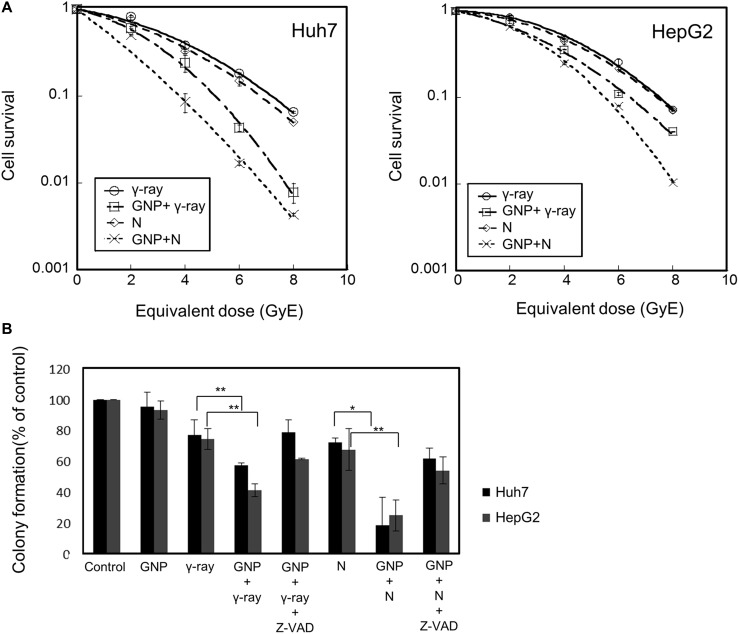
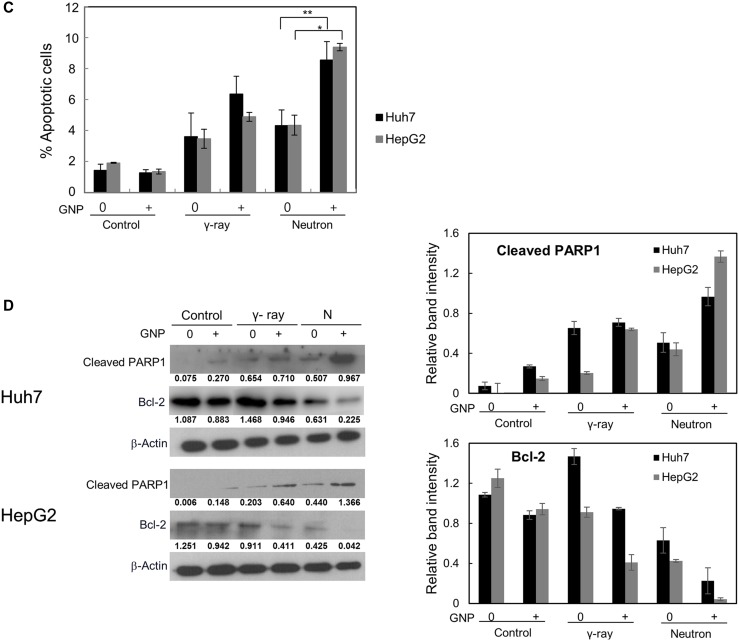
Figure 2. Radiosensitizing effects of gold nanoparticles.
(A) Colony-forming assays of Huh7 and HepG2 cells treated with 1 mM gold nanoparticles and irradiated with γ-rays and neutrons. Values are the means ± SD from three experiments. The x-axis shows the equivalent dose, expressed as GyE (Gray equivalent). (B) Partial abrogation of gold nanoparticle radiosensitization by a pan-caspase inhibitor. Cells were treated with 1 mM gold nanoparticles alone (4 h prior to radiation) or in combination with z-VAD-fmk (10 μM, 6 h prior to radiation). The absorbed doses were 5 Gy for γ-rays and 5 GyE for neutrons. Effect of z-VAD-fmk on gold nanoparticle radiosensitization was assessed by clonogenic survival assay. Values represent the means ± SDs of three experiments; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001. (C) Apoptosis in Huh7 and HepG2 cells, as measured by annexin V staining 48 h after irradiation with 5 Gy of γ-rays or 5 GyE neutrons in the presence or absence of gold nanoparticles. Values represent the means ± SDs of three experiments; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001. (D) Immunoblotting of cell lysates with indicated antibodies. The absorbed doses were 5 Gy for γ-rays and 5 GyE for neutrons. Band intensities for target proteins were normalized to that for β-actin. Values represent the means of 3 experiments ± SD.