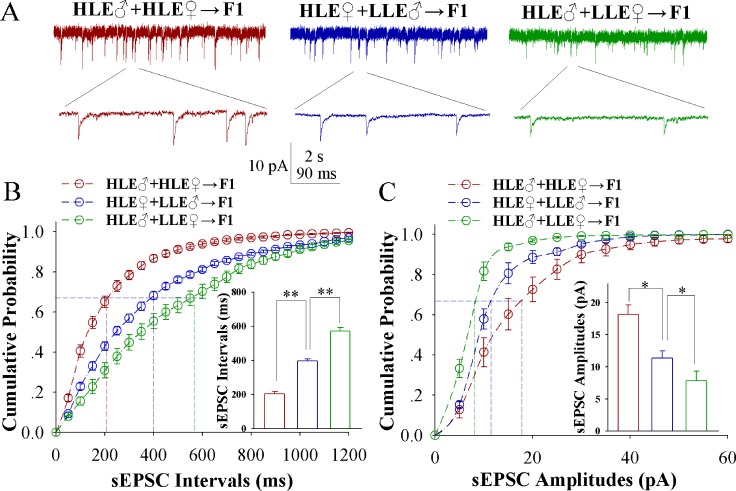
Figure 2. Excitatory synaptic transmission on barrel cortical glutamatergic neurons increases after pairing WS and OS, especially in the F1 mice with the high efficiency of odorant-induced whisker motion from the HLE parents.
Spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSC) were recorded on the YFP-labeled glutamatergic neurons in cortical slices under voltage-clamp (holding potential at -70 mV) in presence of 10 μM bicuculline, in which three F1 groups were studied in training day 6. (A) illustrates sEPSCs recorded on the neurons in CR-formation F1 mice from cross-matings of HLE mice (HLE♂+HLE♀, red trace), HLE female mice and LLE male mice (HLE♀+LLE♂, blue) as well as HLE male mice and LLE female mice (HLE♂+LLE♀, green). Calibration bars are 10 pA, 2 second (top) and 90 ms (bottom). (B) shows cumulative probability versus sEPSC interval in the neurons from CR-formation F1 mice from the cross-matings of HLE mice (HLE♂+HLE♀, red symbols), HLE female mice and LLE male mice (HLE♀+LLE♂, blue) as well as HLE male mice and LLE female mice (HLE♂+LLE♀, green). Insert figure shows the comparisons of sEPSC intervals at 67% cumulative probability from three groups of mice (n = 15 neurons from 8 mice for each group). (C) shows cumulative probability versus sEPSC amplitudes in the neurons from CR-formation F1 mice from the cross-matings of HLE mice (HLE♂+HLE♀, red symbols), HLE female mice and LLE male mice (HLE♀+LLE♂, blue) as well as HLE male mice and LLE female mice (HLE♂+LLE♀, green). Insert figure denotes the comparisons of sEPSC amplitudes at 67% cumulative probability from three groups of mice (n = 15 neurons from 8 mice for each group). An asterisk shows p < 0.05, two asterisks show p < 0.01 and three asterisks show p < 0.001, in which the statistical comparisons are one-way ANOVA.