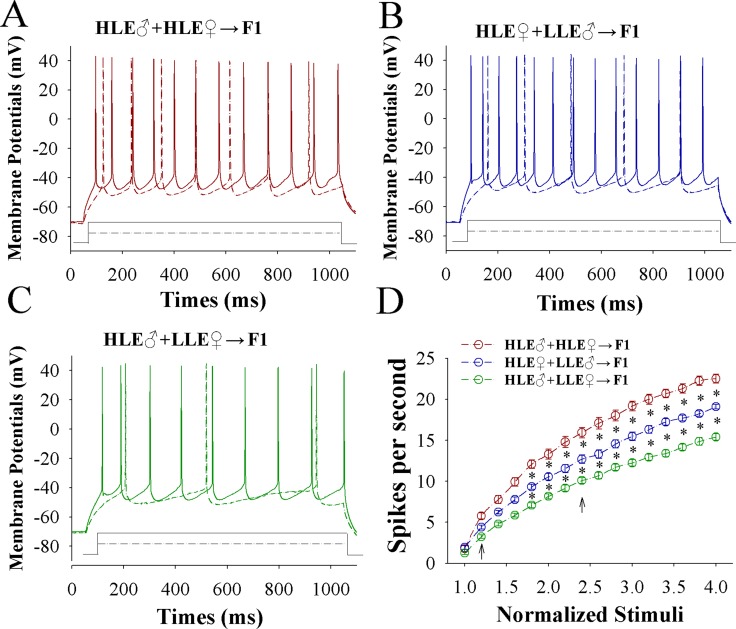
Figure 3. The capability to encode spikes on barrel cortical glutamatergic neurons increases after pairing WS and OS, especially in F1 mice with the high efficiency of odorant-induced whisker motion from the HLE parents.
Sequential spikes were induced by depolarization pulses under current-clamp recording on YFP-labeled glutamatergic neurons in cortical slices. (A) illustrates the spikes induced by two-steps of depolarization pulse on the neurons in a CR-formation F1 mouse from the cross-mating of HLE mice (HLE♂+HLE♀). (B) illustrates the spikes induced by two-steps of depolarization pulse on the neurons in a CR-formation F1 mouse from the cross-mating of HLE female mice and LLE male mice (HLE♀+LLE♂). (C) shows the spikes induced by two-steps of depolarization pulse on the neurons in a CR-formation F1 mouse from cross-matings of HLE male mice and LLE female mice (HLE♂+LLE♀). Solid lines and dash lines present the spikes induced correspondent depolarization pulses, respectively. (D) shows spikes per second versus normalized stimuli in F1 mice from cross-matings of HLE mice (HLE♂+HLE♀, red symbols), HLE female mice and LLE male mice (HLE♀+LLE♂, blue) as well as HLE male mice and LLE female mice (HLE♂+LLE♀, green; n = 15 neurons from 8 mice for each group). Asterisks indicate statistical comparisons between two neighboring groups. An asterisk shows p < 0.05, two asterisks show p < 0.01 and three asterisks show p < 0.001, in which the statistical comparisons are two-way ANOVA.