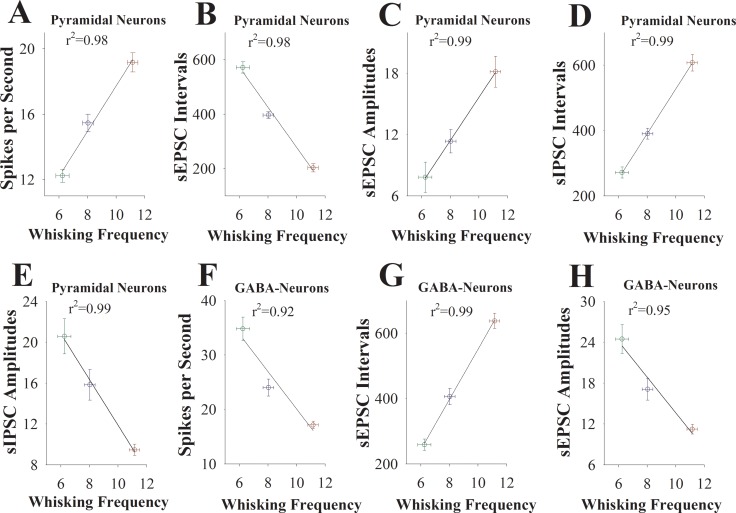
Figure 7. The activity strengths of barrel cortical glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons are linearly correlated with the efficiency of odorant-induced whisker motion in F1 mice.
(A) shows a correlation between spike per second on glutamatergic neurons and whisking frequency induced by the odor-test. (B) illustrates a correlation between sEPSC intervals on glutamatergic neurons and whisking frequency. (C) shows a correlation between sEPSC amplitudes on glutamatergic neurons and whisking frequency. (D) shows a correlation between sIPSC intervals on glutamatergic neurons and whisking frequency. (E) illustrates a correlation between sIPSC amplitudes on glutamatergic neurons and whisking frequency. (F) illustrates a correlation between spike per second on GABAergic neurons and whisking frequency. (G) illustrates a correlation between sEPSC intervals on GABAergic neurons and whisking frequency. (H) illustrates a correlation between sEPSC amplitudes on GABAergic neurons and whisking frequency. Data points for F1 mice that were from HLE male and female parents are red symbols. Data points for F1 mice that were from HLE female and LLE male are blue symbols. Data points for F1 mice that were from HLE male and LLE female are green symbols.