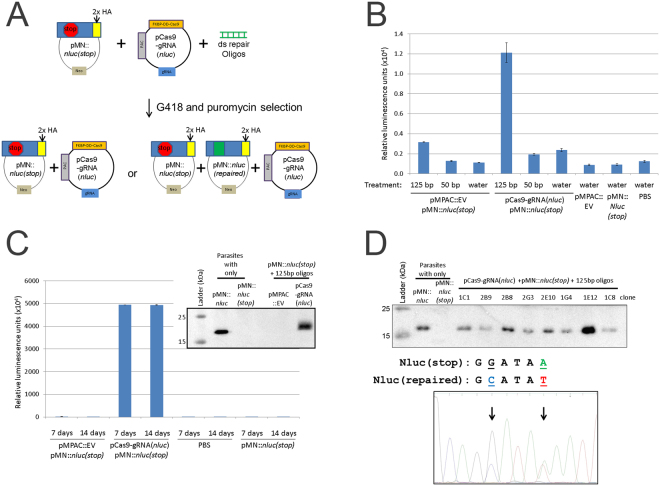
Figure 4.
Transient transfection, selection and screening for nanoluciferase repair. (A) Cartoon representation of transient nanoluciferase repair activity assay followed by selection with puromycin and G418. (B) A total of 5 × 107 parasites were nucleofected with 10 μg of pCas9-gRNA(nluc), 10 μg pMN::nluc(stop) and 100 μg of either 50 bp or 125 bp annealed repair oligos or water using T-cell buffer (Lonza) and the U-033 program (Amaxa). Parasites were immediately recovered in completed TYM media + 1 μM Shield-1. After 24 hours of recovery, equivalent numbers of parasites (1 × 106) were assayed for nanoluciferase activity and the graph represents the average relative luminescence value +/− standard deviation from duplicate samples for each condition (C). After 24 hours of recovery, one transfection population of the pMPAC::EV- and pCas9-gRNA(nluc)-treated parasites from Fig. 4B was treated with 30 μg/ml puromycin and 50 μg/ml G418 to select for parasites transfected with both plasmids. After 7 and 14 days (post-nucleofection), parasites were re-tested for nanoluciferase activity by assay of equivalent numbers of parasites (1 × 106). The graph represents the average relative luminescence value +/− standard deviation for each condition. Inset: Anti-HA epitope immunoblot analysis of control samples (pre-selected parasites) compared to protein isolated from puromycin/G418 selected parasites grown for two weeks. (D) Upper: anti-HA epitope immunoblot analysis of controls (pre-selected plasmids) and representative clones from 14 day puromycin/G418 selected pCas9-gRNA(nluc) + pMN::nluc(stop) + 125 bp oligo parasites in Fig. 4C. Lower: representative DNA sequencing trace (Genewiz sequencing and FinchTV sequence viewer) of PCR products amplifying the nanoluciferase gene from T. vaginalis genomic DNA preparations. Highlighted (and arrows) are residues G50C and A54T which are the site of the two predicted modifications for repair of the stop codon (A54T) and oligo-modification confirmatory mutation (G50C). Immunoblot analyses in Fig. 4C and D were imaged using a Bio-Rad Gel Doc and ImageLab software. Full length blots/gels are presented in Supplementary Figure S5.