Figure 1.
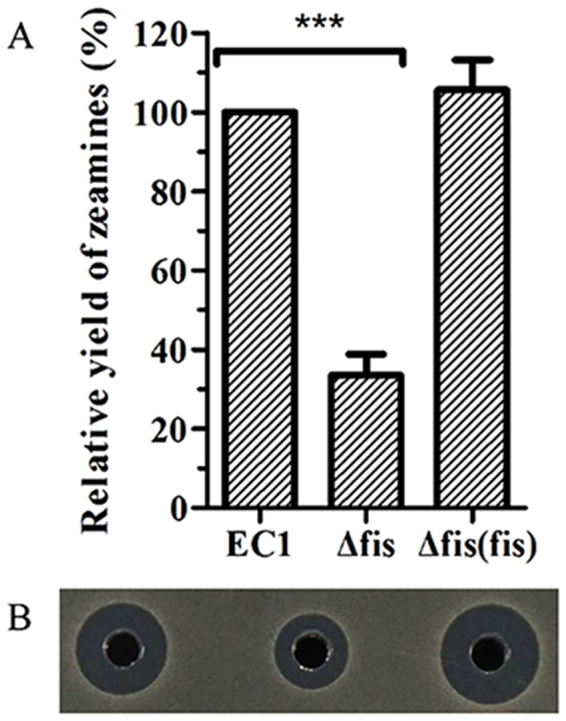
The null Fis mutation decreased the antimicrobial activity of D. zeae strain EC1. (A) Quantitative analysis of zeamine yield of wild-type strain EC1 and its derivative strains. The antimicrobial activity bioassay plates were prepared by pouring 15 mL of LB agar medium into the 120 × 120 mm plates, and then overlaid with 20 mL of 1% agarose containing 1.0 × 108 cells of fresh E. coli harboring pBBR1MCS4 plasmid. Wells of 5 mm in diameter were punched after solidification. Overnight bacterial cultures were grown in LS5 medium to OD600 at around 1.4, which was centrifuged twice at 12,000 rpm for 10 min, and 20 μl of the supernatants were added into the wells. The plates were incubated at 37 °C for 10 h. The antimicrobial activity was determined by measuring the radius of the visible clear zone surrounding the well. The concentration of zeamines was determined by this formula: zeamines (unit) = 0.5484e0.886x (R2 = 0.9957), X is the radius in millimeters of the inhibition zone surrounding the well. (B) Plate assay of the antimicrobial activities of wild-type strain EC1 and its derivative strains. The photograph was taken after 12 h of incubation at 37 °C. Final results of fis mutant were normalized to that of the wild-type EC1, which was set to a value of 100%, for easy comparison. Experiments were repeated at least three times in triplicates. Symbol: ***P < 0.0001 (Student’s t-test).
