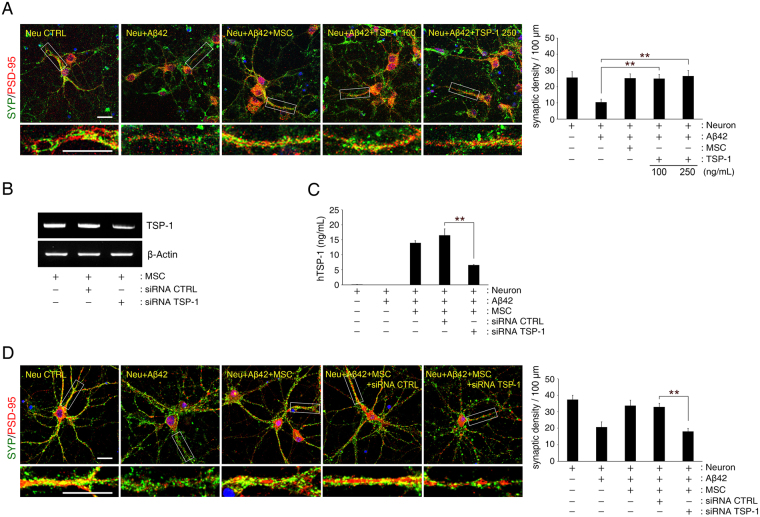
Figure 3.
Aβ42 peptide-mediated synaptic dysfunction is mitigated by TSP-1 in hippocampal neurons. (A) Representative images of hippocampal neurons stained for pre-synaptic (SYP, green) and postsynaptic (PSD-95, red) proteins (Scale bar = 25 μm). Bottom insets (white boxes) show higher magnification. Quantification of synaptic density (number of synapses per 100 μm of dendritic length, n ≥ 30 dendrites) revealed that treatment with recombinant human TSP-1 protected hippocampal neurons from Aβ42 peptide-induced synaptic dysfunction (mean ± SEM, **p < 0.005 versus Aβ peptide-treated hippocampal neurons). (B,C) TSP-1-siRNA was transfected into hUCB-MSCs overnight, after which the cells were co-cultured with hippocampal neurons for 3 days. hUCB-MSCs were separately transfected with scrambled siRNA as a control. mRNA expression of TSP-1 was (B) analysed with RT-PCR, and (C) the relative quantity of secreted TSP-1 was determined using ELISA (mean ± SEM, **p < 0.005 versus control-siRNA-treated hUCB-MSCs). (D) Representative images of hippocampal neurons stained for pre-synaptic (SYP, green) and post-synaptic (PSD-95, red) proteins (Scale bar = 25 μm). Bottom insets (white boxes) show higher magnification. Quantification of synaptic density (number of synapses per 100 μm of dendritic length, n ≥ 30 dendrites) revealed that hUCB-MSCs with knockdown of TSP-1 by siRNA were not protected from Aβ42 peptide-induced synaptic dysfunction in hippocampal neurons. (mean ± SEM, **p < 0.005 versus control-siRNA-treated hUCB-MSCs).