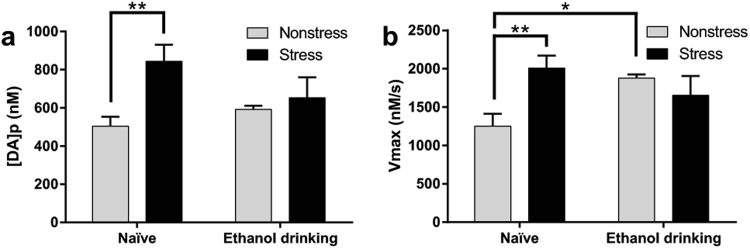
Figure 3.
Prior ethanol drinking alters effects of social-defeat stress on DA dynamics in rat nucleus accumbens. Stressed subjects showed significantly higher DA release per stimulus pulse compared to nonstress control (A, left panel). Prior ethanol exposure completely blunted this effect (A, right panel). Both stress (B, left panel) and ethanol exposure (B, right panel) significantly increased accumbal DA uptake, measured as the V max. However, there was no significant difference between subjects exposed to defeat stress episodes and ethanol (B, left panel). Data presented as mean ± SEM and analyzed by a two-way ANOVA. A single slice was taken from each subject in every experimental group for FSCV recordings. The number of subjects for naïve nonstressed: n = 10; for naïve stressed: n = 9; for ethanol drinking and nonstressed: n = 5; for ethanol drinking and stressed: n = 5. *p < 0.5; **p < 0.01.