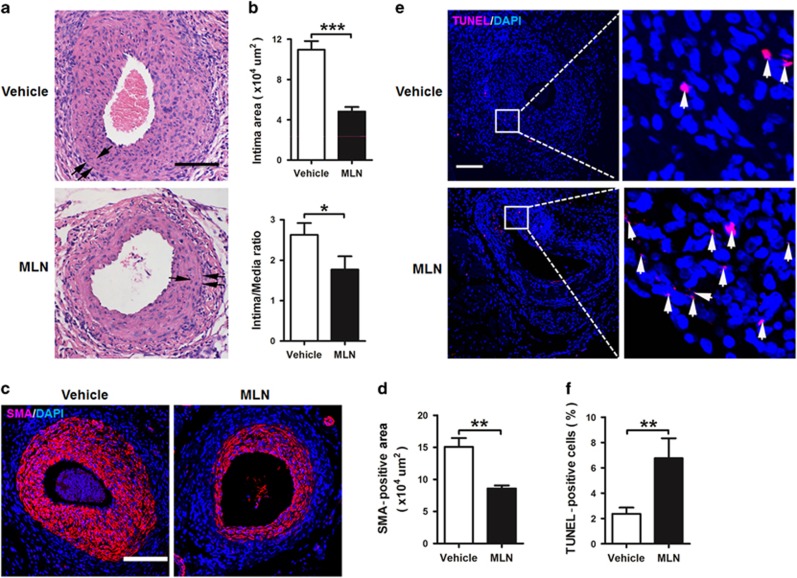
Figure 1.
MLN4924 inhibits arterial injury-induced neointimal hyperplasia in mice. (a) Representative hematoxylin and eosin staining of cross-sections of femoral arteries from wire-injured C57 mice that were treated with vehicle or MLN4924 (MLN) for 28 days. Single arrows indicate internal elastic lamina and double arrows indicate external elastic lamina. (b) Quantifications of intimal area and intima/media ratio. (c) Representative immunofluorescence staining of α-smooth muscle actin (SMA) in injured arteries. (d) Quantification of SMA-positive cells. (e) Representative TUNEL staining of injured arteries. Arrows denote TUNEL-positive cells. (f) Quantification of TUNEL index as percentage of apoptotic cells. All scale bars: 280 μm. n=6. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001