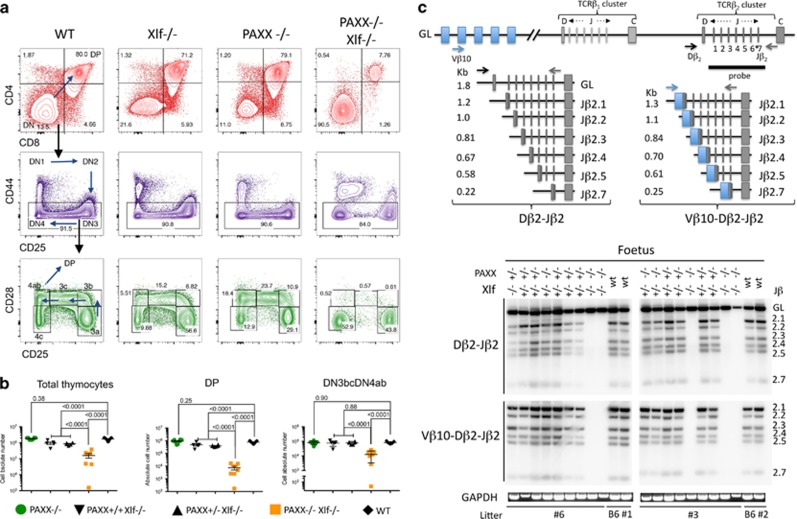
Figure 4.
V(D)J recombination defect and impaired development of thymocytes in PAXX−/−/Xlf−/− E18.5 embryos. (a) Immunostaining of thymocytes from wt, Xlf−/−, PAXX−/−, and PAXX−/−Xlf−/− E18.5 embryos. Upper panel (red) shows the important decrease in CD4+CD8+ DP in the thymus from PAXX−/−Xlf−/− embryos. DN (CD4−CD8−CD3−) thymocytes were subdivided into DN1–DN4 according to the expression of CD44 and CD25 (middle panel). Lower panel (green) shows the severe block at the transition DN3a (CD44−CD25+CD28−) to DN3b (CD44−CD25+CD28+) in PAXX−/−Xlf−/− embryos. B220+CD19+ FL cells were analyzed for the expression of CD43 that marks pro-B cells (middle panel). In the lower panel, cells were gated on the CD43+B220+CD19+ population and analyzed for iIgM expression. (b) Quantification of thymocyte subpopulations in the various PAXX/Xlf genotypes. Mann–Whitney test was used for statistical analysis. (c) PCR strategy to analyze TCRβ rearrangement according to Gartner et al.29 and autoradiogram of PCR products revealed with the TCR-Jβ probe demonstrating the absence of either Dβ-Jβ or VβDβJβ rearrangements in thymocytes from PAXX−/−Xlf−/− embryos. GAPDH-specific PCR was used as loading control