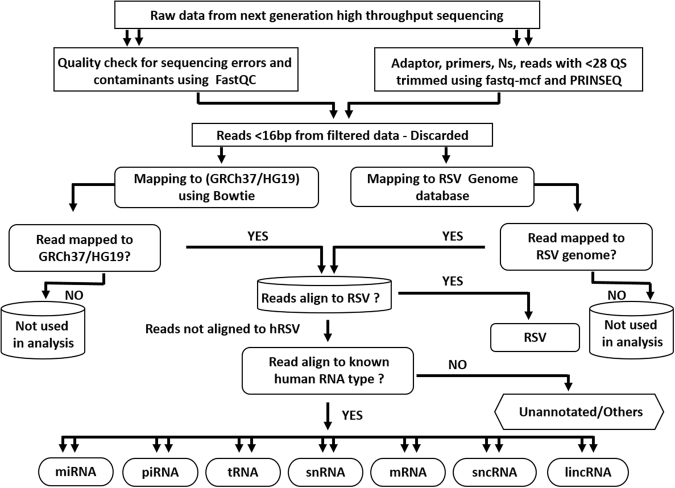
Figure 5.
Next generation high-throughput RNA sequencing analysis pipeline flowchart. The flowchart demonstrates how the next generation sequencing data was analyzed. In brief, raw sequencing reads were quality checked for sequencing errors and contaminants using FastQC. Adapter sequences, primers, Ns, and reads with quality score below 28 were trimmed using fastq-mcf of ea-utils and PRINSEQ. Reads < 16 bp after trimming were discarded. Pseudo single-end reads were mapped to the human genome using bowtie. Raw read counts were calculated for known gene categories including ncRNAs, antisense transcripts, coding and intronic regions of mRNAs, and repeats. Annotations of known genes were retrieved from miRBase release 20, NCBI RefSeq, Human lincRNA Catalog, and UCSC Genome Browser. hRSV- Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus, miRNA- microRNA, piRNA- piwi interacting RNA, tRNA- transfer RNA, snRNA- small nucleolar RNA, mRNA-messenger RNA, sncRNA-small noncoding RNA, lincRNA- long intergenic noncoding RNA.