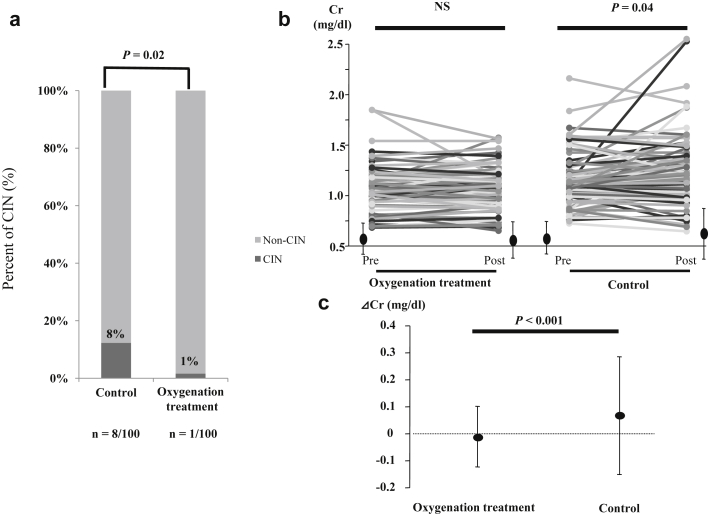
Figure 1.
(a) Contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) incidence between study groups. CIN incidence was significantly lower in the oxygenation treatment group than in the control group (1/100 [1%] vs. 8/100 [8%], odds ratio = 0.12, 95% confidence interval = 0.01–0.95, P = 0.02). (b) Changes in serum creatinine levels following contrast exposure. Postprocedural serum creatinine levels increased in the control group (1.08 ± 0.25 mg/dl to 1.15 ± 0.31 mg/dl, P = 0.04) but remained unchanged in the oxygenation treatment group (1.08 ± 0.21 mg/dl to 1.07 ± 0.19 mg/dl, P = 0.714). (c) Median and interquartile range of serum creatinine levels before and after cardiovascular angiography. The average change in serum creatinine levels was significantly lower in the oxygenation treatment group than in the control group (−0.01 ± 0.12 mg/dl vs. 0.07 ± 0.24 mg/dl, P < 0.001). Data are presented as mean ± SD. NS, not significant.