Figure 4.
SCH9 Efficiently Transduces Neural Stem Cells in the Subventricular Zone
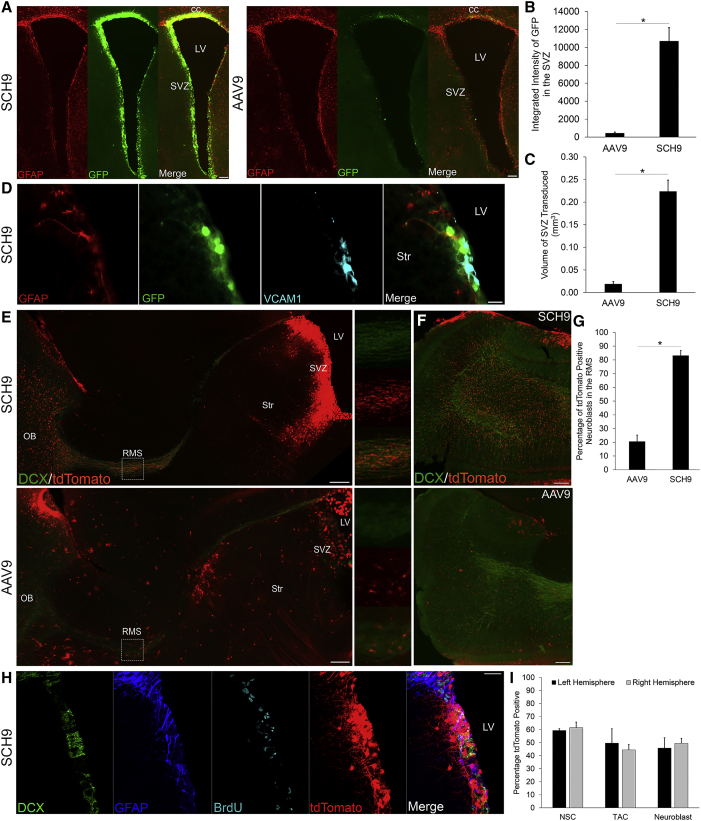
(A) SCH9 strongly transduces the SVZ contralateral to the injection site. Coronal sections were stained for GFAP (red) and GFP (green). Scale bars indicate 100 μm. (B and C) SCH9 mediates higher GFP fluorescence intensity (B) and transduction volume (C) in the SVZ than AAV9. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 3. Statistical difference of *p < 0.005 by two-tailed Student’s t test. (D) Neural stem cells infected with SCH9 express GFP (green) and the neural stem cell markers GFAP (red) and VCAM1 (blue) in coronal sections. Scale bar indicates 20 μm. (E) Labeling of tdTomato-positive migrating neuroblasts in the SVZ-RMS-OB pathway 30 days post-injection of SCH9 (top) or AAV9 (bottom) expressing Cre recombinase in Ai9 floxed STOP tdTomato mice. Sagittal sections were stained for the neuronal migration protein doublecortin (DCX, green), and tdTomato fluorescence (red) is native. Dashed rectangles indicate the region of the rostral migratory stream that is magnified in the right panels. Scale bars indicate 200 μm. (F) TdTomato-positive neuroblasts in multiple stages of radial migration and differentiation into granule cells were observed in the olfactory bulb (top: SCH9, bottom: AAV9). Sagittal sections were stained for DCX (green), and tdTomato fluorescence (red) is native. Scale bars indicate 200 μm. (G) SCH9 transduction results in a higher percentage of DCX+/tdTomato+ neuroblasts in the rostral migratory stream than with AAV9. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 4–5. Statistical difference of *p < 0.005 by two-tailed Student’s t test. (H) Representative images of marker colocalization with BrdU+ cells. Sagittal sections were stained for DCX (green), GFAP (blue), BrdU (cyan), and tdTomato (red). Scale bar indicates 50 μm. (I) Quantification of BrdU+/GFAP+ NSCs in the left and right hemispheres. Data are presented as mean ± SD; n = 5. CC, corpus callosum; LV, lateral ventricle; OB, olfactory bulb; RMS, rostral migratory stream; SVZ, subventricular zone; Str, striatum.