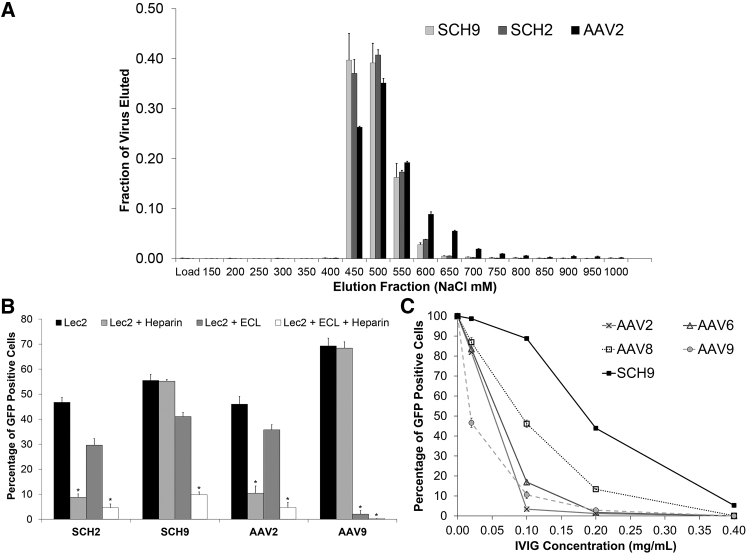
Figure 6.
Characterization of SCH9 Glycan Binding and Resistance to Neutralizing Antibodies
(A) SCH9 and SCH2 bind a heparin column with similar affinity as AAV2. Samples were loaded onto a heparin affinity column and eluted with increasing NaCl concentration. The load fraction represents the virus recovered in the column flow-through after sample loading in 150 mM NaCl. Data are represented as mean ± SD; n = 3. (B) SCH9 utilizes both galactose and heparan sulfate proteoglycans for cell entry. Both HSPG and galactose receptors must be blocked to prevent SCH9 infection of Lec2 cells. The controls AAV2 and AAV9 utilize HSPG and galactose, respectively. A modest decrease in infectivity was observed after addition of ECL in all samples, potentially because of steric blocking of receptors on the cell surface. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 3. Statistical difference of *p < 0.005 by two-tailed Student’s t test. (C) SCH9 is less susceptible to neutralizing antibodies than the parent serotypes AAV2, AAV6, AAV8, and AAV9. Data are presented after being normalized to the fraction of GFP-expressing cells in the absence of IVIG as mean ± SEM; n = 3.