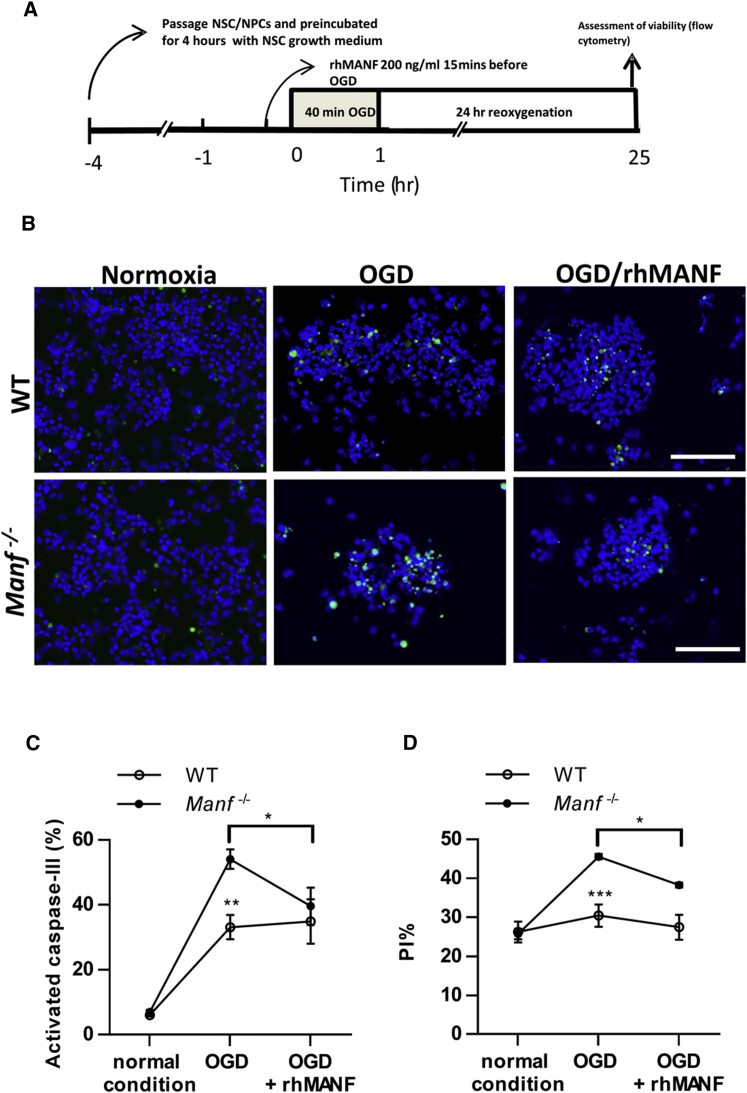
Figure 3.
MANF Is Protective against OGD in NSCs
(A) Timeline of the oxygen-glucose-deprivation/reperfusion experiment. (B) Representative photomicrographs of activated caspase-3 labeling in the NSCs after OGD or under normal conditions. (C) Ratio of activated caspase-3+ cells in relation to DAPI+ nuclei. Increase in activated caspase-3 density in Manf−/− cells after OGD treatment compared to WT cells. rhMANF treatment before OGD decreased activated caspase-3 density in Manf−/− cells (n = 6–11, two-way ANOVA, genotype X condition effect p = 0.042; **p < 0.01 genotype effect; *p < 0.05 Manf−/− OGD versus OGD + rhMANF). (D) Analysis of cell death by PI labeling. The percentage of PI+Manf−/− nuclei after OGD and reoxygenation was higher than in WT cells, indicating a greater apoptotic rate in Manf−/− cells. OGD-induced Manf−/− cell death was prevented by rhMANF treatment (n = 6 to 7, two-way ANOVA, genotype X condition effect p = 0.001; ***p < 0.001 genotype comparison; *p < 0.05 Manf−/− OGD versus OGD + rhMANF). Scale bar, 100 μm (B). Data are presented as mean ± SEM.