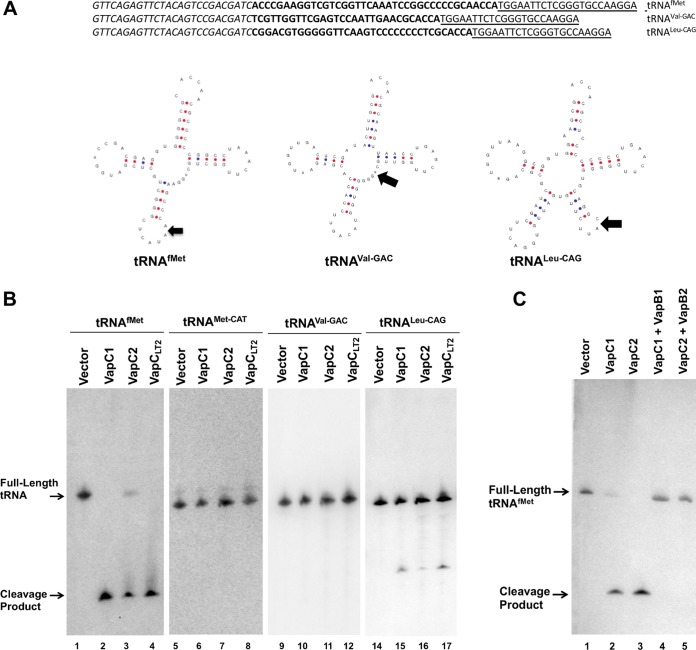
FIG 3.
VapC1NTHi and VapC2NTHi cleave the tRNAfMet anticodon loop. (A) Sequences and structure diagrams of tRNAs identified by RNA sequencing as potential VapC cleavage products. Italic and underlined sequences show the 5′ and 3′ adaptors, respectively, and those in bold show the identified cleavage fragments. On each tRNA diagram, an arrow indicates the site of cleavage based on sequencing results. (B) Northern blot analysis of total RNA from E. coli BW25113Δ6 carrying pBAD, pBAD-VapC1, pBAD-VapC2, or pBAD-VapCLT2 (induced with 0.2% l-arabinose), as described in Materials and Methods. Blots were probed with radiolabeled oligonucleotides specific to the tRNAs listed above the panels. Full-length or cleaved tRNAs are indicated with arrows. (C) Northern blot analysis of total RNA from E. coli BW25113Δ6 carrying pBAD, pBAD-VapC1, or pBAD-VapC2 or expressing each toxin coexpressed with its cognate antitoxin (pJSB31-VapB1-sfGFP or pJSB31-VapB2-sfGFP), as described in Materials and Methods. Blots were probed with a radiolabeled oligonucleotide specific for tRNAfMet. Full-length or cleaved tRNAfMet is indicated with an arrow.