FIG 7.
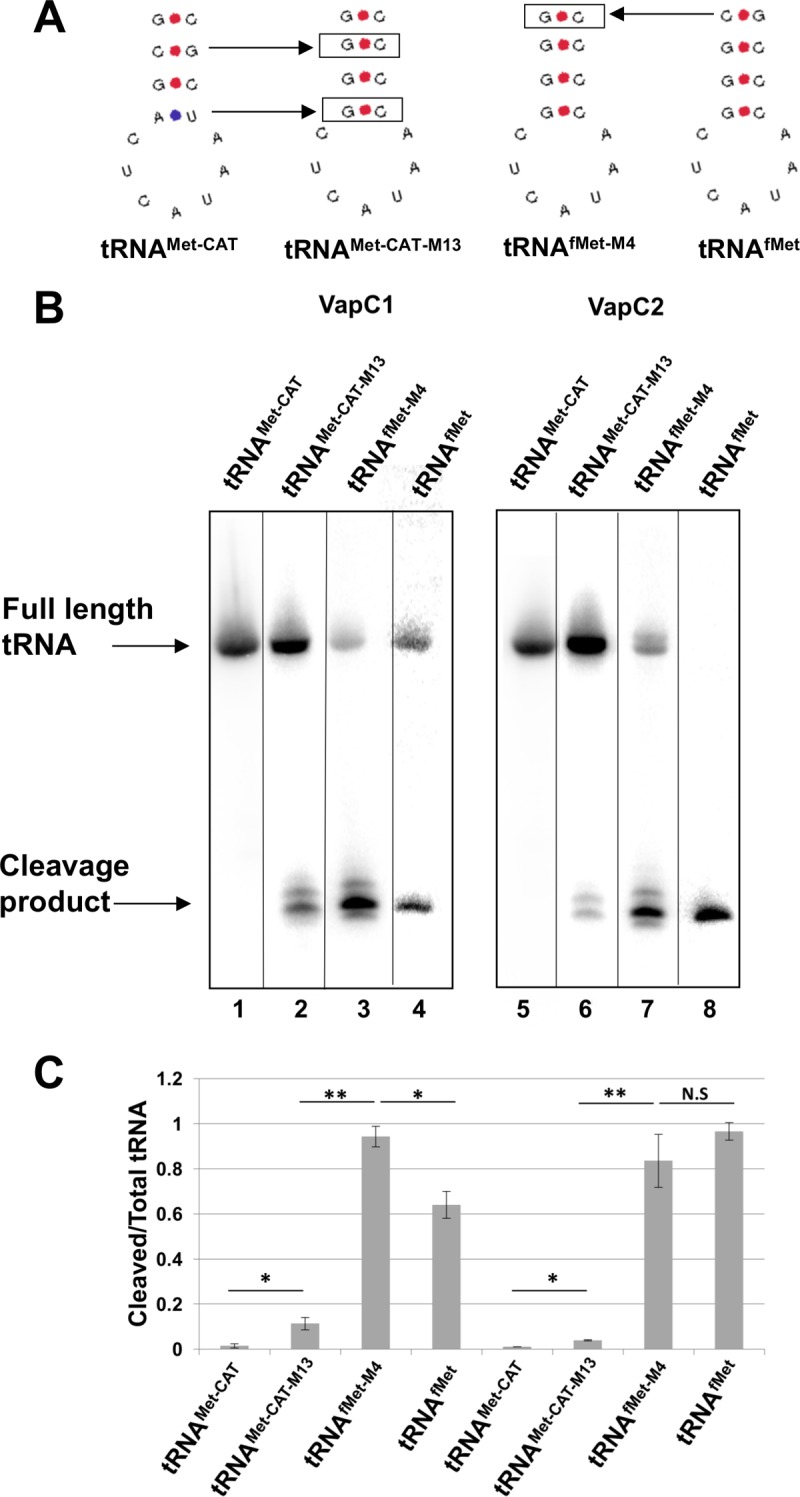
Efficient cleavage of tRNAfMet by VapC1NTHi and VapC2NTHi requires key base pairs in the anticodon stem structure. (A) Diagram showing anticodon stem-loop sequences and structures of tRNAs and mutants. Boxed base pairs indicate mutations made from either tRNAMet-CAT or tRNAfMet. (B) Differential hybridization Northern blot analysis of total RNAs isolated from E. coli BL21(DE3) cells expressing the VapC1 (left) or VapC2 (right) toxin (induced with 0.01% l-arabinose) and tRNAs (induced with 0.5 mM IPTG) as indicated, performed as described in Materials and Methods. The blots were hybridized with an oligonucleotide specific to both E. coli tRNAfMet or tRNAMet-CAT and the mutant tRNA, but with one nucleotide mismatch for the wild-type tRNA. After hybridization of the probe, blots were washed at 42°C and then again at 68°C. The image is a composite, as each tRNA required hybridization of a different oligonucleotide. Complete images may be seen in Fig. S1 in the supplemental material. (C) Quantification of cleaved tRNA/total tRNA from Northern blots, measured using ImageQuant. The data are averages for two biological replicates, and error bars represent standard deviations. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; N.S, not significant.
