Fig. 2.
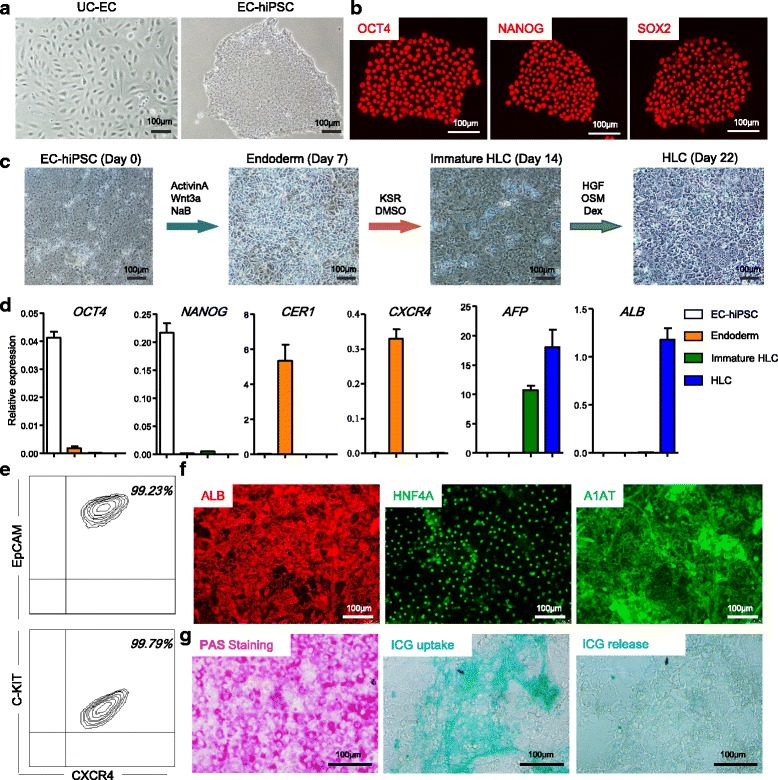
Single donor-derived hiPSCs reprogrammed from UC-ECs with efficient hepatic differentiation capacity. a Morphology of single donor-derived UC-ECs and EC-hiPSCs under phase-contrast microscopy. Scale bar, 100 μm. b Immunocytochemical detection of pluripotency factors OCT4, NANOG, and SOX2 in EC-hiPSCs. Scale bars, 100 μm. c Schematic illustration of the hepatic differentiation process and morphology of EC-hiPSCs, definitive endoderm, immature HLCs, and HLCs during differentiation. Scale bars, 100 μm. d Expression of pluripotency factors (OCT4 and NANOG), definitive endoderm-related genes (CER1 and CXCR4), an immature HLC-related gene (AFP), and an HLC-related gene (ALB) in EC-hiPSCs, definitive endoderm, immature HLCs, and HLCs, as determined by qPCR (n = 4 each). e Flow cytometry analysis of cells expressing EpCAM, CXCR4, and C-KIT among EC-hiPSC-derived definitive endoderm. f Immunocytochemical detection of the hepatic markers ALB, HNF4A, and A1AT in EC-hiPSC-derived HLCs. Scale bars, 100 μm. g Glycogen storage was detected by PAS staining (left), and ICG uptake and release (right) were analyzed in EC-hiPSC-derived HLCs. Scale bars, 100 μm. ALB albumin, EC endothelial cell, HGF hepatocyte growth factor, hiPSC human induced pluripotent stem cell, HLC hepatic-like cell, ICG indocyanine green, PAS periodic acid–Schiff, UC umbilical cord, OSM Oncostatin M, Dex Dexamethasone, KSR Knockout serum replacement, DMSO Dimethyl sulfoxide
