Fig. 4.
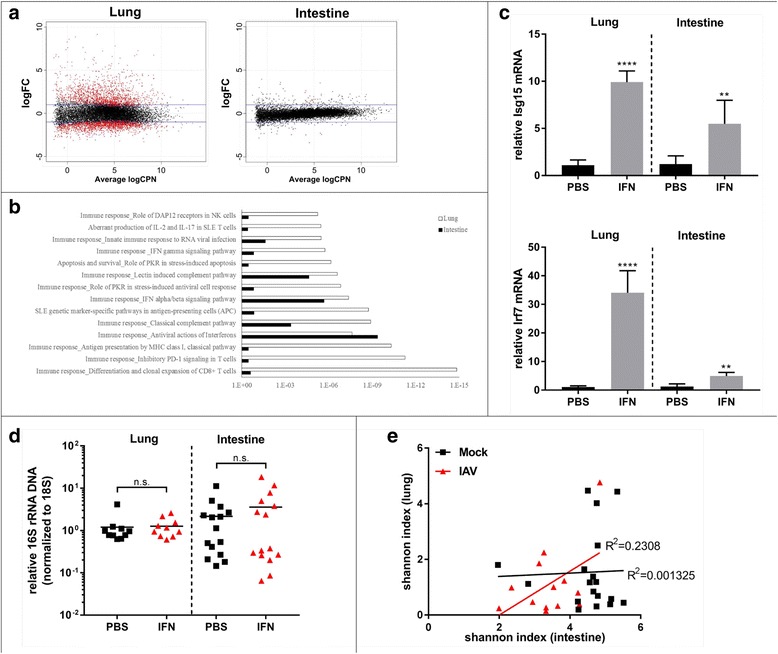
Influenza A virus infection provokes a robust antimicrobial host response in the LRT with less pronounced effects on the small intestine. a MA-plots of differentially expressed mRNAs in IAV-infected vs. mock-treated animals. Blue lines indicate twofold threshold; dots represent average n-fold expression values over mock (log2 scale, p value < 0.05) of mRNAs from 4 individual IAV-infected mice, 7 days post treatment. RNAseq results from three or four individual mice (mock or IAV, respectively) from lung tissue are depicted on the left, from small intestine on the right. b Gene ontology of significantly enriched pathways. White bars represent p values for lung-enriched pathways of upregulated mRNAs based on RNAseq results of IAV infected over mock. Black bars represent small intestine-enriched pathways. c n-fold induction of ISG15 and IRF7 24 h after IFN-α B/D treatment in lung and small intestine (n = 5 per group). d n-fold changes in 16S/18S from three independent experiments for SI (n = 15 per group) and two independent experiments for LRT (n = 10 per group). Median is indicated for each experimental group. e Correlation of alpha diversity of lung and intestinal samples for individual mice 7 dpi. Respective R2 values and regression fit are indicated
