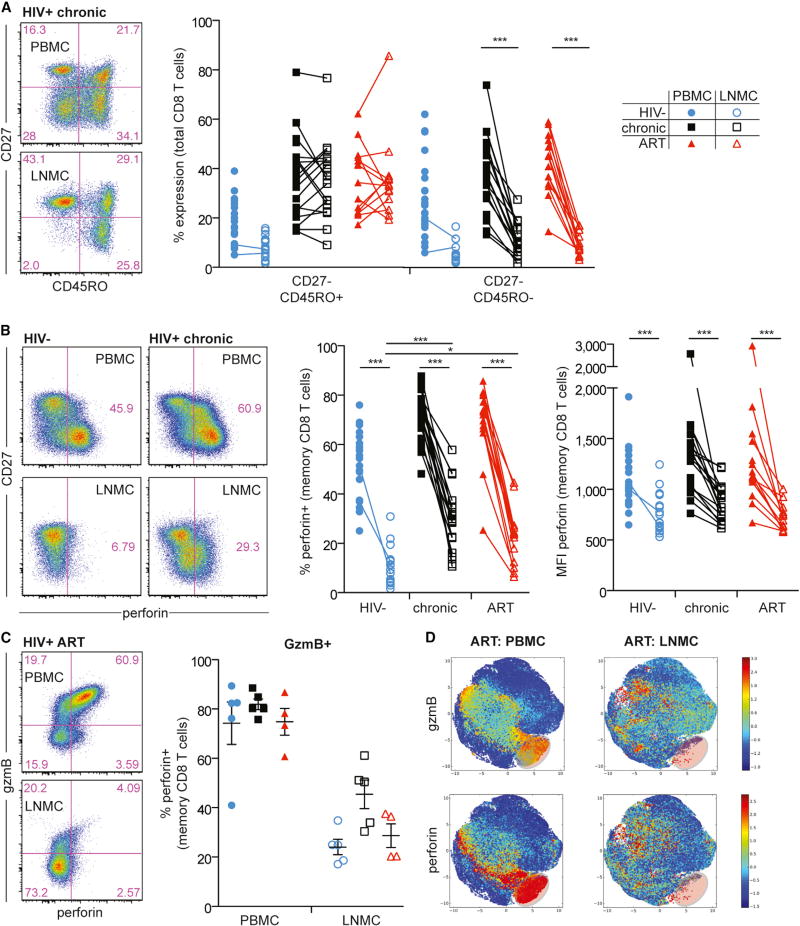
Figure 1. HIV Infection Induces Accumulation of Effector Memory CD8+ T Cells with Low Levels of Perforin Expression in LNs.
(A) Representative flow plots (left) showing CD3+ CD8+ T cells in PBMCs (top) and LNMCs (bottom) from a chronically infected HIV+ individual, and a comparison of memory subsets (right) in PBMCs versus LNMCs.
(B) Representative flow plots (left) showing memory CD8+ T cell expression of perforin in PBMCs (top row) versus LNMCs (bottom row) from an HIV− individual versus a chronically infected HIV+ individual. Perforin frequency and MFI in memory CD8+ T cells in PBMCs versus LNMCs is shown on the right for HIV−, chronic HIV+, and ART-treated HIV+ individuals.
(C) Representative flow plots (left) showing perforin versus gzmB expression in PBMCs (top) versus LNMCs (bottom) from an ART-treated HIV+ individual, and frequency of perforin co-expression in gzmB+ memory CD8+ T cells (right) in PBMCs versus LNMCs.
(D) Cell ACCENSE tSNE plots of perforin and gzmB expression in memory CD8+ T cells comparing PBMCs and LNMCs from ART-treated HIV+ individuals (based on n = 4/group). The highlighted area in lower right of each tSNE plot represents cytolytic effector CD8+ T cells.
The statistical tests used were the Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-test (for between-subject groups within a tissue compartment), the Mann-Whitney test (for within a subject group between tissue compartments), and the Wilcoxon matched-pairs two-tailed test (for paired samples). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Blue circle, open blue circle, HIV−; black square, open black square, HIV+ therapy naive; red triangle, open red triangle, HIV+ on ART. Ranges shown on plots represent mean ± SEM. In all figures, closed symbols represent PBMCs and open symbols represent LNMCs. Memory subsets were determined by CD27 and CD45RO expression patterns.