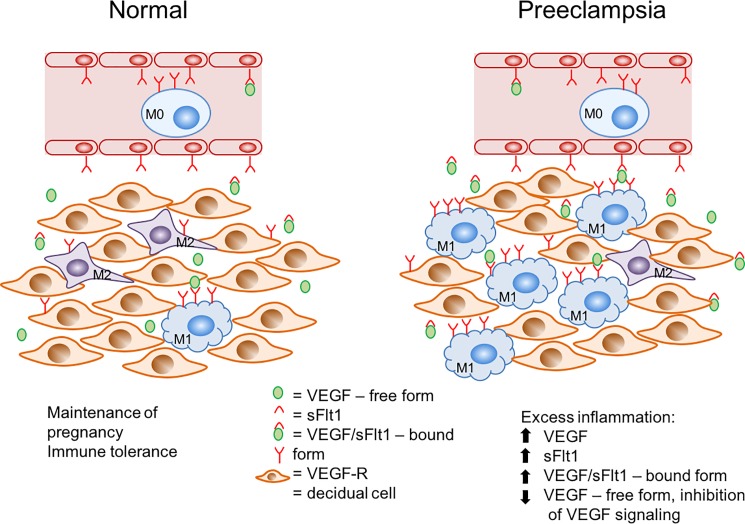
Fig 6. Model of VEGF action on decidual macrophages.
Decidual stromal cells produce VEGF, which acts to recruit monocytes and tissue macrophages to the site of implantation in normal pregnancy. It also acts to polarize macrophages to the M2 phenotype. In preeclampsia, however, there is an increase in VEGF, which may enhance recruitment of macrophages to the decidua. Excess VEGF at the implantation site in preeclamptic pregnancies may also stimulate excess production of sFlt1 by trophoblast cells (22, 23), leading to complete inhibition of VEGF signaling (lack of free VEGF; increase in VEGF-sFlt1 bound form), and ultimately resulting in the failure of differentiation of macrophages to the M2 phenotype and accumulation of large numbers of M1 cells in the placental bed.