Neuroradiologic examinations of leukoencephalopathies with molecular markers
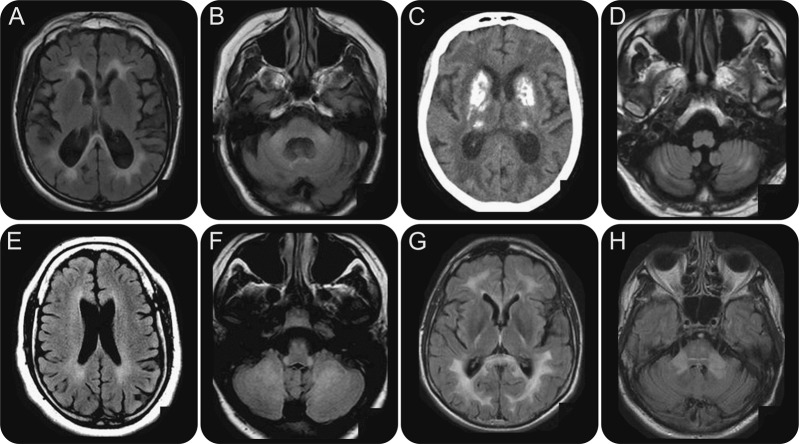
Figure 4. (A, B) Fragile X–associated tremor/ataxia syndrome. Axial fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR): hyperintensities involve the splenium of the corpus callosum (A) and the middle cerebellar peduncles (B). (C, D) Mitochondrial disorders. (C) CT scan. Bilateral and profound calcifications. (D) Axial FLAIR MRI: hyperintensities of the cerebellar white matter. (E) Spastic paraplegia–11. Axial FLAIR sequence: subtle hyperintensities of the periventricular white matter. (F) Leukoencephalopathy with brainstem and spinal cord involvement and lactate elevation syndrome. Axial FLAIR sequence: hyperintense signal of the inferior cerebellar peduncles, pyramidal tracts, and cerebellar white matter. (G, H) Adult-onset autosomal dominant leukodystrophy. Axial FLAIR sequences: hyperintensities of the splenium of the corpus callosum, corticospinal tracts (G), and middle cerebellar peduncles (H).