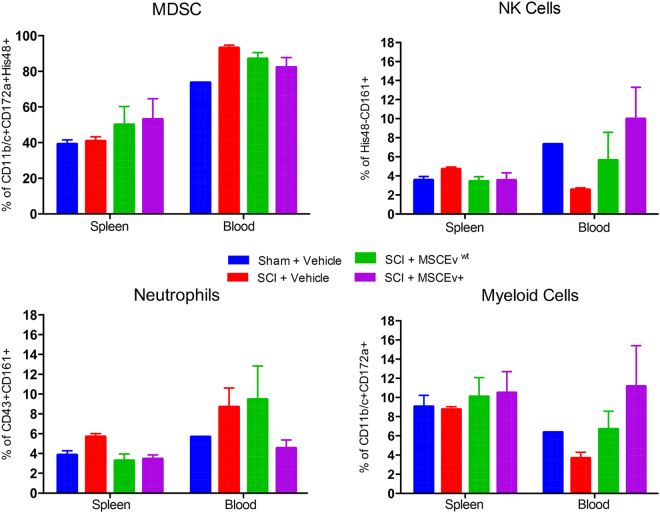
Figure 5.
Flow cytometry of spleen tissue and blood samples from each animal provide evidence of anti-inflammatory effects of MSCEvwt/MSCEv+ treatment. Animals treated with either MSCEvwt or MSCEv+ after SCI show approximately 5–10% decrease in MDSC present in the blood with an increase of approximately 10% in the spleen. This suggests that MSCEvwt/MSCEv+ treatment causes a retention of MDSCs in the spleen that normally migrate to the blood after SCI. The opposite appears to occur with NK cells. MSCEvwt and MSCEv+ treatment both result in a decrease of NK cells in the spleen following SCI but restore blood levels of NK cells to sham values. Both treatments also resulted in a decrease in splenic neutrophils, however, MSCEv+ caused a decrease in blood neutrophils to sham-like values. Both treatments recover myeloid cells that are decreased in both spleen and blood following SCI. Sham + Vehicle, n = 2, SCI + Vehicle, n = 2, SCI + MSCEvwt, n = 3, SCI + MSCEv+, n = 3.