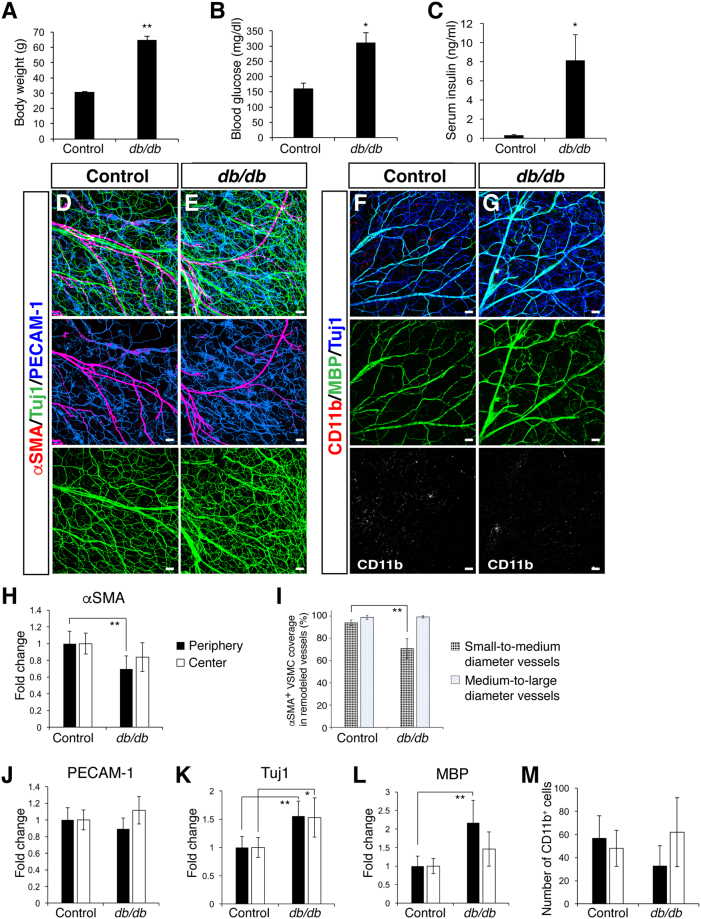
Figure 5.
Vascular and neuronal abnormalities in the outer ear skin of adult db/db mice. (A) Male control and db/db mice (n = 3–4 per group) were analyzed at 36 weeks-of-age. A significant increase in body weight was found in db/db mice. (B) Blood glucose level was elevated in the db/db mice after fasting at 36 weeks-of-age. (C) Serum insulin level was elevated in the db/db mice after fasting at 36 weeks-of-age. (D,E) Triple labeling with αSMA (red) together with Tuj1 (green) and PECAM-1 (blue) shows a reduction in VSMC coverage (red) and an increase in Tuj1+ nerves (green) in the db/db mutants. (F,G) Triple labeling with CD11b (red) together with MBP (green) and Tuj1 (blue) shows an increase in MBP+ myelin sheath and Tuj1+ nerves (blue) in the db/db mutants, while there was no increase in CD11b+ inflammatory cells (red). (H–M) Quantification measurements of αSMA+ VSMC coverage (H,I), PECAM-1+ vascular density (J), and the amount of Tuj1+ nerves (K), MBP+ myelin sheath (L) and the number of CD11b+ inflammatory cells (M). At least three regions in the peripheral and central region of each outer ear skin were analyzed and the result was shown as a fold change (H,J–L). The degree of αSMA+ VSMC coverage as a percentage of the total length of small-to-medium and medium-to-large diameter remodeled blood vessels was analyzed (I). Data are presented as mean ± S.E.M. Astersisks indicate statistical significance (*P < 0.05; **p < 0.01) according to a two-tailed Student’s t test. Scale bars, 100 µm.