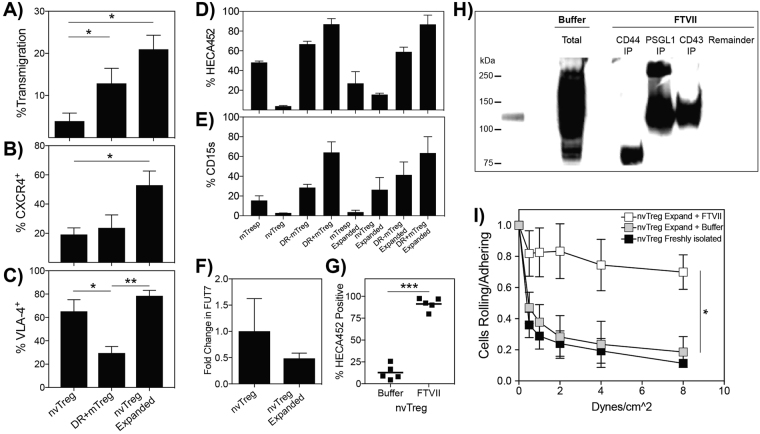
Figure 4.
Exofucosylation increases expression of selectin ligands on nvTregs and their endothelial adherence. Freshly isolated nvTregs and effector DR+mTregs, and 14-day in vitro expanded nvTregs were tested for their ability to (A) undergo static transendothelial migration (TEM) towards SDF-1 in a Boyden Chamber assay, and to express surface (B) CXCR4, and (C) VLA-4. All T cell subsets, isolated from three donors, were stained pre- and post-expansion to determine expression of sLeX as detected by (D) HECA452 or (E) CD15 s. (F) Pre- and post- ex vivo expanded nvTregs were examined for their relative expression of FUT7 RNA by RT-PCR. (G) Buffer- or fucosyltransferase VII-treated expanded nvTregs were stained to determine HECA452/sLex expression. (H) The proteins that bind mE-selectin-Ig in buffer- or FTVII-treated expanded nvTregs were identified by performing sequential immunoprecipitation on lysates with anti-CD44, anti-PSGL-1, and then anti-CD43, and detecting the proteins that bound mE-selectin-Ig by western blotting. The blot in Fig. 4H was not cropped as the samples were run in the order as shown. (I) Buffer-treated and FTVII-treated expanded nvTregs, and freshly isolated nvTregs were examined for their ability to roll and adhere to endothelium in the presence of dynamic shear forces. Data shown are mean ± SEM. Significance, determined by Student’s t test, is indicated by (*P < 0.05), (**P < 0.01), and (***P < 0.001).