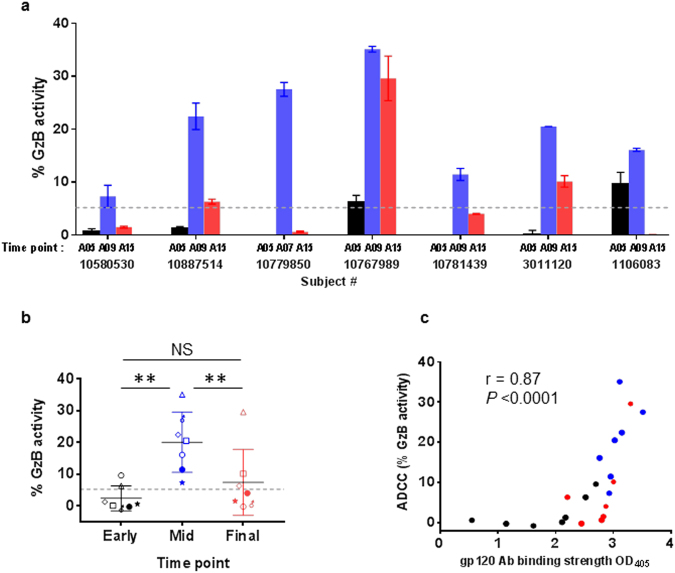
Figure 8.
Induction of ADCC activity in vaccine recipients. Antibody-dependent cellular cytolysis (ADCC) activity was measured using CEM.NKr-CCR5 target cells coated with SF162 gp140 (5 µg/100,000 cells/sample), labeled with TL4 dye, and treated with diluted plasma (1:200) and with rhesus CD16+ human NK KHYG-1 effector cells at an effector/target ratio of 5:1. The mixtures were then suspended in a granzyme B (GzB) substrate for 30 min at 37 oC. GzB delivered into target cells by effector cells was detected with the fluorogenic GzB substrate and visualized by flow cytometry. ADCC was calculated based on percentage of GzB+ target cells above negative control. Cut-off value (dotted line) was determined as the mean plus 3 standard deviations of % GzB+ cells in pooled prebleed plasma. (a) ADCC activities were measured in plasma of 5 VAX003 and 2 VAX004 vaccinees collected at early (A05, after 2 vaccine doses), mid- (A07 or A09, after 3 or 4 doses), and final (A15, after 7 doses) time points. Averages and standard deviation of duplicate wells from an experiment are shown. (b) ADCC activity was detected at mid-time points (A07 or A09) but declined at A15. **P > 0.01; by the paired 2-tailed t test. (c) ADCC activity strongly correlated with anti-gp120 Ab levels detected in ELISA. Correlation analysis was performed using the nonparametric Spearman test.