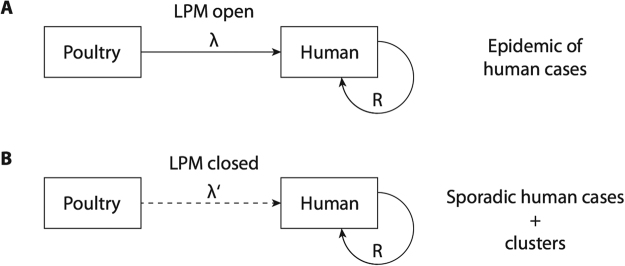
Figure 1.
Conceptualisation of the modeling approach. Panel A shows the situation when LPMs are open, and H7N9 transmission from poultry to humans occurs at a rate λ, while human-to-human transmission also occurs with reproductive number Re. In this situation there may be an epidemic of human infections with H7N9. Panel B shows the situation when LPMs are closed, transmission from poultry to humans occurs at a reduced rate λ′, while human-to-human transmission also occurs with the same reproductive number Re as in panel A. In this situation there may be sporadic clusters of human infections with H7N9.