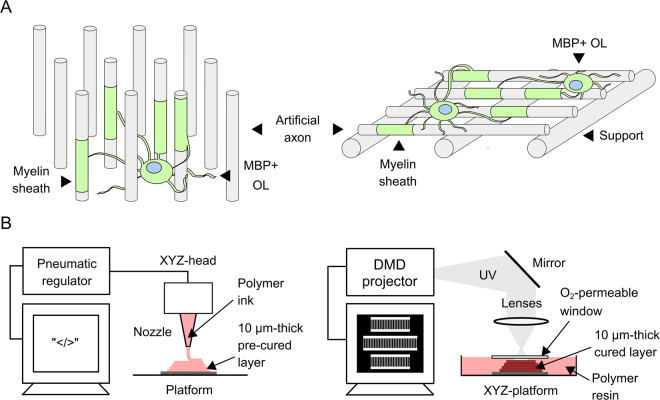
Figure 1.
Schematic of artificial axons and additive manufacturing approaches. (A) Arrays of vertical fibers (left) of uniform diameter in close proximity resemble geometry of neuronal axon bundles and white matter tracts, and enable complete wrapping around fiber circumference, while allowing fast detection of concentric myelin. Suspended horizontal fibers (right) allow high throughput acquisition of myelin segment length. (B) Direct ink printing (left): inks are extruded through a nozzle on a translational head to fabricate predefined three-dimensional constructs. Projection micro-stereolithography (right): slices of computer-aided design (CAD) models are sequentially sent to a digital micromirror device (DMD) illuminated by a light source, and projected sequentially onto a photopolymer resin bath.