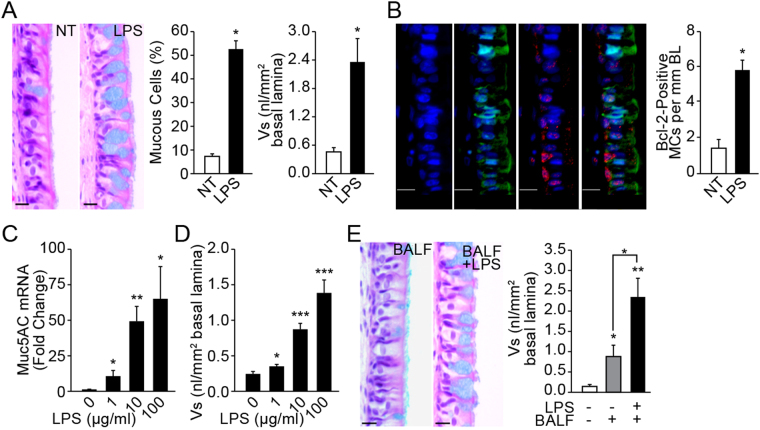
Figure 1.
LPS exposure increases inflammatory factors in the BAL that augment Muc5AC and Bcl-2 expression. (A) LPS induced mucous cell metaplasia in rat nasal epithelium. Representative micrographs of nasal epithelia from non-treated (NT) and LPS-instilled rats stained with AB-PAS. Quantification of mucous cells and volume density of intraepithelial stored mucosubstances (Vs) at 3 d post LPS instillation. Data shown as mean ± SEM (n = 7/group) (B) LPS-induced Bcl-2 expression in mucous cells. A representative nasal epithelial section from LPS-treated rat showing Bcl-2-immunopositivity (red) among Muc5AC-positive (green) mucous cells (MCs) and the nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). (C) MUC5AC mRNA levels in LPS-treated organ cultures quantified by q-PCR. The fold-change over non-treated controls is shown. (D) Quantity of the intraepithelial stored mucosubstances (Vs) in LPS-treated organ cultures stained with AB-PAS. (E) Representative photomicrographs of nasal explants treated with BALF from LPS-instilled rats or with BALF and 100 µg/ml LPS (BALF+LPS), and the quantity of Vs in explants at 24 h following each treatment. Data shown as mean ± SEM (n = 3/group); *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.