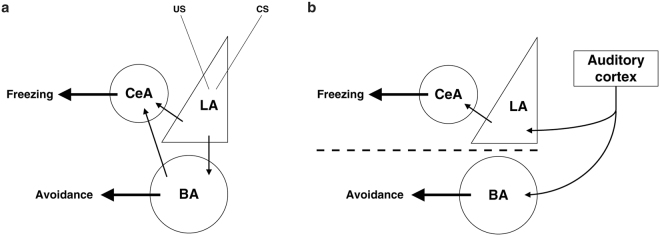
Figure 6.
Two models of information processing in the amygdala. (a) The traditional model of information flow within the amygdala proposes that during the formation of fearful memories the LA is the input area for both conditioned (CS) and unconditioned (US) stimulus information. From this site, information is conveyed either directly or indirectly (through the BA) to the CeA (Adapted from Amorapanth et al., 2000). (b) The new model detailing the proposed neural circuits engaged within the amygdala during the long-term auditory fearful memory expression. In this model, the amygdala receives two independent and parallel inputs. One arrives at LA and through the CeA it supports freezing behavior in response to the aversive CS. The other input arrives at BA and drives the ability of rats to bias their actions away from the CS. The latter circuit operates independent from LA and CeA. In addition, we propose that essential information regarding auditory fearful memories arrives at either LA or BA from the auditory cortex (AC).