Fig. 1.
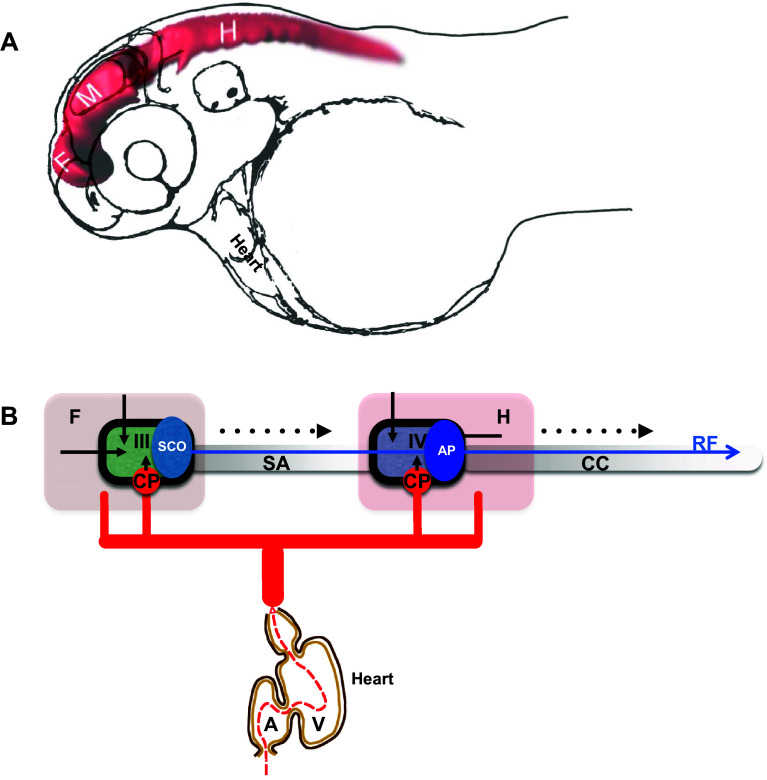
Development of the brain ventricular system of zebrafish. a The dye-filled ventricular system of 48 hpf zebrafish consists of three distinct cavities, which are reshaped as two ventricles and sylvius aqueduct connecting these. b Hypothetical scheme connecting the zebrafish blood circulation and the brain ventricular systems. During development influx of eCSF inflates and shapes the brain ventricular system [50, 51]. The choroid plexi contribute CSF enriched by ions, micronutrients and proteins. The SCO produces substances of the Reissner fiber, etc. A atrium, AP area postrema, CC central canal, CP choroid plexus, F forebrain, H hindbrain, M midbrain, SA Sylvius aqueduct, SCO subcommissural organ, V heart ventricle, III III brain ventricle, IV IV brain ventricle. Black arrow indicates embryonic CSF influx, arrowhead indicates CSF influx, broken line indicates direction of CSF flow. Blue arrow indicates Reissner fiber, red solid lines indicates vasculature and black solid line indicates ependyma