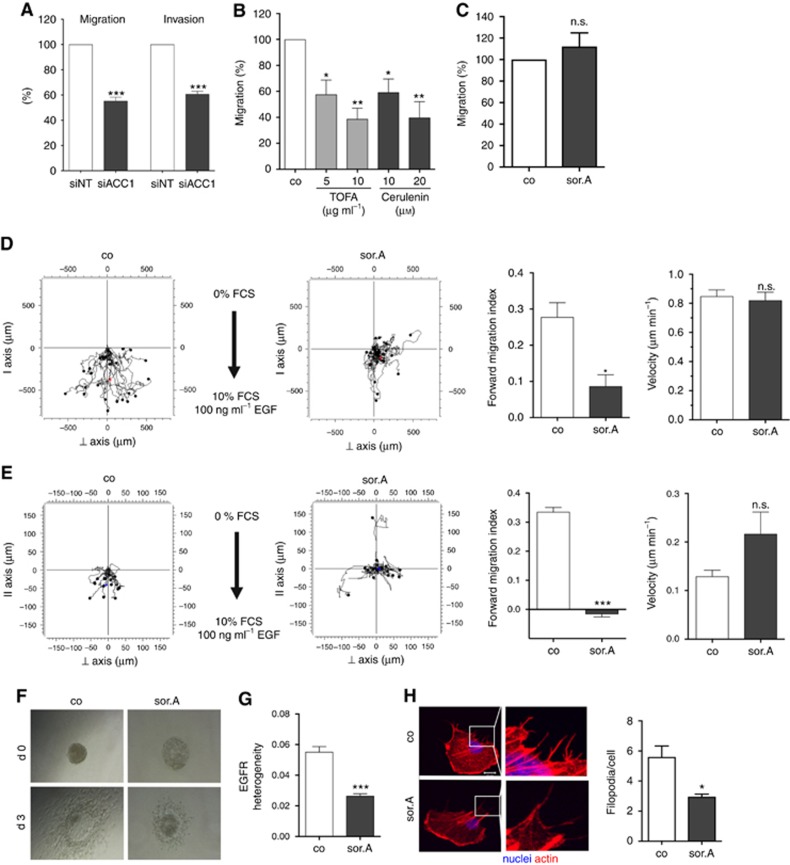
Figure 3.
Inhibition of cancer cell migration and invasion by pharmacological targeting of fatty acid synthesis pathway. (A) MDA-MB-231 cells were transfected with siRNA against ACC1 and scrambled control, respectively. Migratory and invasive potential of the cells was analysed in transwell assays. (B) Treatment with increasing concentrations of the ACC1 inhibitor TOFA and FASN blocker Cerulenin for 72 h strongly diminishes the migration capacity of MDA-MB-231 cells, (C) whereas impeding ACC1 activity by 1 μM soraphen A has no effect on the mammary epithelial cell line MCF10a. (D) Chemotactic migration and (E) invasion of soraphen A-treated MDA-MB-231 cells (1 μM) towards FCS and EGF was investigated by using 2D and 3D chemotaxis slides. Forward migration index and velocity of the cells is shown on the right. (F) T24 bladder carcinoma spheroids were embedded in collagen and invasion of the cells towards FCS as chemoattractant was monitored over 3 days. (G) Migrating MDA-MB-231 cells treated with or without 1 μM soraphen A were stained with EGFR antibody and localisation of the receptor within the cells was investigated. Heterogeneity was analysed using ImageJ. (H) MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with 1 μM soraphen A for 2 h, detached and reseeded. After 2 h cells were fixed and stained with rhodamine phalloidin. Quantification of the number of filopodia is depicted on the right. Error bars show the s.e.m. of three different experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t test: n.s. = non-significant, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.