Figure 3.
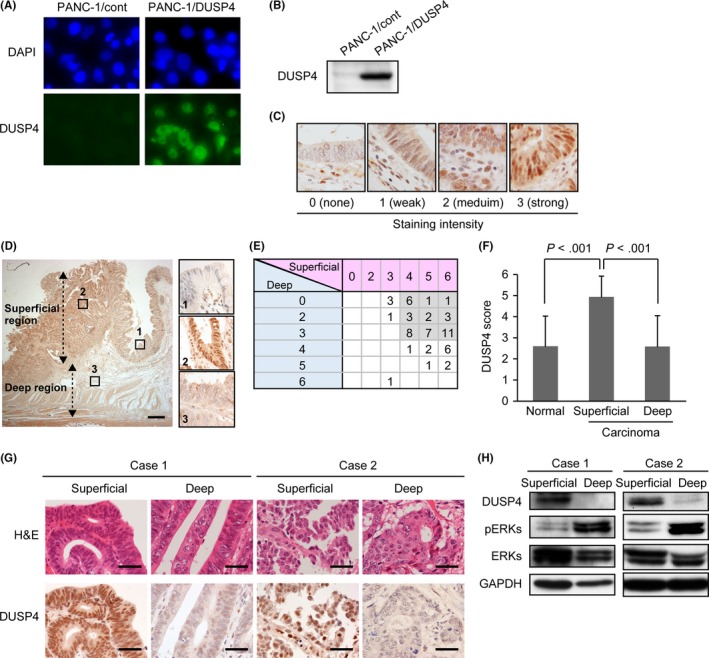
Expression of dual‐specificity phosphatase 4 (DUSP4) is upregulated in the superficial region of colorectal cancer (CRC) tissues, but downregulated in the deep region. A, Validation of a novel rabbit anti‐DUSP4 polyclonal antibody using PANC‐1 cells stably re‐expressing DUSP4 (PANC‐1/DUSP4‐1) and its control clones (PANC‐1/cont), which express only the blasticidin resistance gene. Representative images of immunocytochemistry using DAPI and the anti‐DUSP4 antibody. The antibody specifically recognized the nucleus of PANC‐1/DUSP4‐1 but not that of PANC‐1/cont. B, Specificity of the antibody was further determined by Western blot analysis using lysates of PANC‐1/cont and PANC‐1/DUSP4‐1. The antibody specifically detected DUSP4 protein in PANC‐1/DUSP4‐1. C, Representative images of immunohistochemistry for DUSP4 in CRC tissues. The staining intensity in the nucleus of cancer cells was scored as: 0, none; 1, weak; 2, medium; and 3, strong. D, Representative images of immunohistochemistry for DUSP4 in CRC tissues. The insets indicate normal epithelium (1), the superficial region of CRC (2), and the deep region of CRC (3). Scale bar = 1 mm. E, Immunohistochemical DUSP4 scores for 59 CRC cases. In 42 cases (71.2%, gray boxes), DUSP4 was upregulated and downregulated in the superficial region and deep region, respectively. F, DUSP4 score was significantly higher in the superficial region than in normal epithelium, and was significantly lower in the deep region than in the superficial region. Data shown as mean ± SD. G, H & E staining and immunohistochemistry for DUSP4 in frozen tissues from superficial and deep regions in representative CRC cases. In all sections, the proportion of tumor cells included exceeded 70% of the total. Scale bar = 40 μm. H, Expression levels of DUSP4 protein and phosphorylation levels of ERKs (pERKs) in CRC tissues analyzed by Western blotting. DUSP4 expression was downregulated in the deep region relative to the superficial region, whereas ERKs were hyperactivated in the deep region relative to the superficial region
