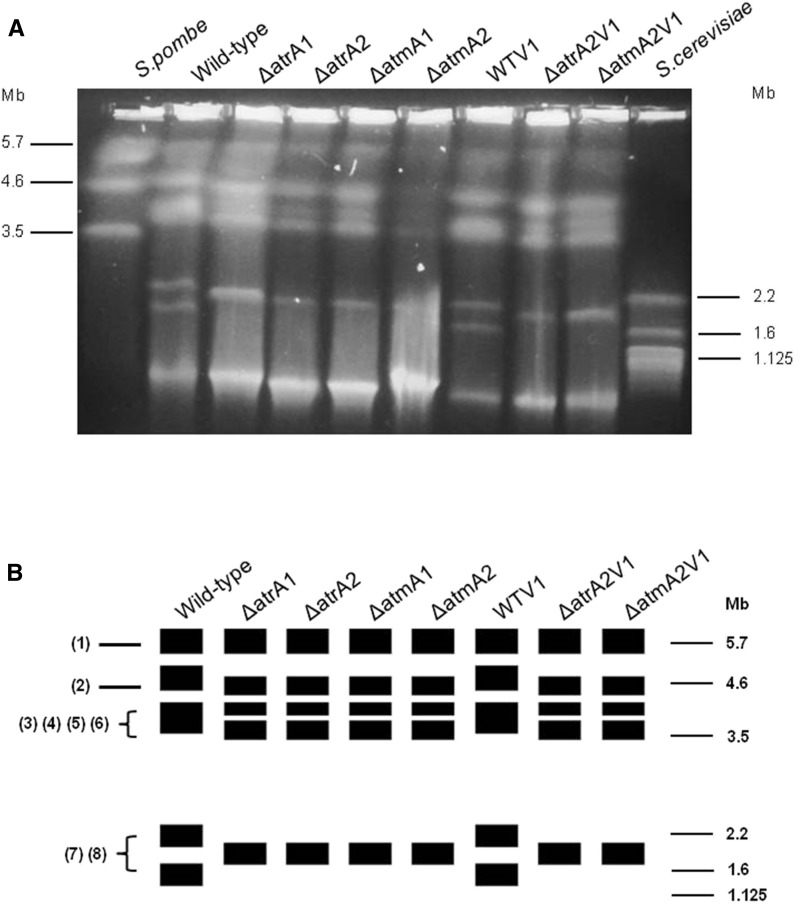
Figure 2.
Karyotype polymorphism between wild-type strain and ΔatmA and ΔatrA mutants of A. fumigatus. (A) Chromosomal bands separated by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and stained with ethidium bromide. A. fumigatus wild-type and mutants have five chromosomal bands. The smallest band (∼1.0 Mb) seen in the wild-type and mutants could correspond to a minichromosome. Sc. pombe and S. cerevisiae chromosomal bands were used as size standards indicated in megabases (Mb) at the right. A. fumigatus strains are: wild-type, mutants ΔatmA1-2, and ΔatrA1-2; and wild-type (WTV1) and mutants (ΔatmA2V1 and ΔatrA2V1) selected after grown with subinhibitory concentration of voriconazole. (B) Diagrammatic representation of karyotypes of wild-type mutants of A. fumigatus. The rectangles represent a unique distinguishable band visualized after staining with ethidium bromide. The thickness of the rectangles represents the proportional staining of each chromosomal band. At the left are indicated the in silico chromosomes of A. fumigatus assigned to the chromosomal bands.