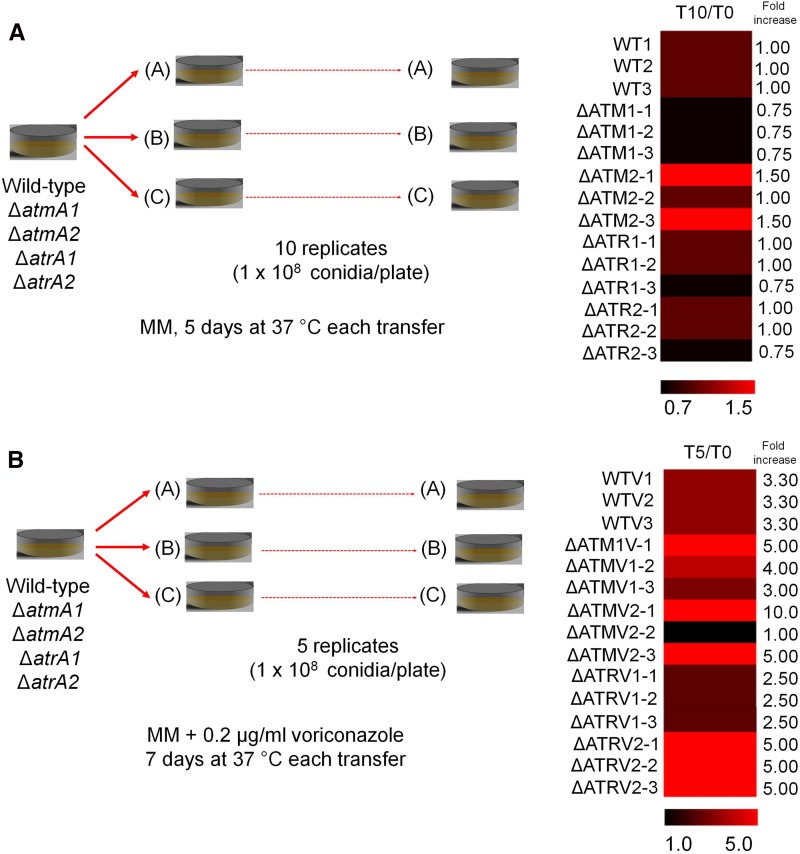
Figure 9.
The A. fumigatus AtmA and AtrA mutants are important for the development of high resistance to voriconazole. (A) Left panel, conidia (1 × 108/plate) of WT0, -1 to -3; ΔAtmA1-0, -1 to -3; ΔAtmA2-0, -1 to -3; ΔAtrA10-1, -1 to -3; and ΔAtrA20-2, -1 to -3 strains were transferred 10 times every 5 d to MM plates and incubated at 37°. Minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) were determined according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (B) (CLSI, M38A2; http://clsi.org/) Left panel: conidia (1 × 108/plate) of WTV0, -1 to -3; ΔATMA1V-0, to -A and -C; ΔATMA2V-0, to -A and -C; ΔATRA1V-0, to -A and -C; and ΔATRA2V-0, to -A and -C strains were transferred five times every 7 d to MM + 0.2 µg of voriconazole plates and incubated at 37°. (A and B) Right panels: MICs values of the strains after 10 and 5 transfers were divided by the parental strains (T10/T0 or T5/T0). Heat map shows the change in MIC values for the evolved strains in the absence or presence of voriconazole.