Figure 1.
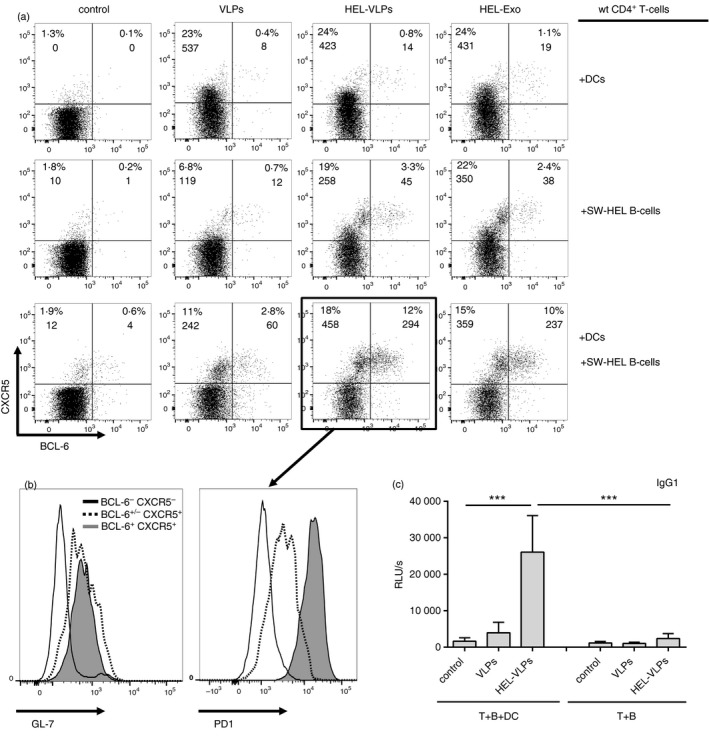
Generation of wild‐type (wt) follicular helper T (Tfh) ‐like cells with T‐helper function after 6‐day co‐culture experiments. CD4+ T cells from naive BL6 mice, B cells from naive SW‐HEL mice and/or splenic dendritic cells (DCs) from BL6 mice were co‐cultured in the presence of hen egg lysozyme–virus‐like particles (HEL‐VLPs), HEL‐Exo or control VLPs without surface HEL. After 6 days of incubation, cells were stained for surface CD4, CXCR5, GL‐7, PD1 and intracellular BCL‐6. The gating strategy is demonstrated in the Supplementary material (Fig. S1). Dot plots (a) and histograms (b) represent singlets of the non‐auto‐fluorescent CD4+ cells. (a) Numbers in the quadrants indicate percentages of the respective subpopulation among the CD4+ cells and cell counts per time package. (b) Histograms represent GL‐7 and PD1 surface expression on subpopulations of CD4+ cells from co‐culture with naive SW‐HEL B cells and DCs from BL6 mice in the presence of HEL‐VLPs. Each experiment was performed three times in duplicates. The data of one representative experiment are shown. (c) Supernatants from SW‐HEL B cells cultured over 6 days with CD4 T cells and +/− DCs (T+B+DC or T+B) in the presence of HEL‐VLPs or VLPs were analysed by ELISA for the presence of anti‐HEL IgG1. The results are presented as relative light units per second (RLU/s). The histograms represent the mean from three independent experiments (two samples each) ± standard deviation. ***p < 0·001; one‐way analysis of variance with Tukey's post test. The data from co‐cultures of CD4+ T cells, DCs, and SW‐HEL B cells (Fig. 1a, bottom row) have been reported previously.6
