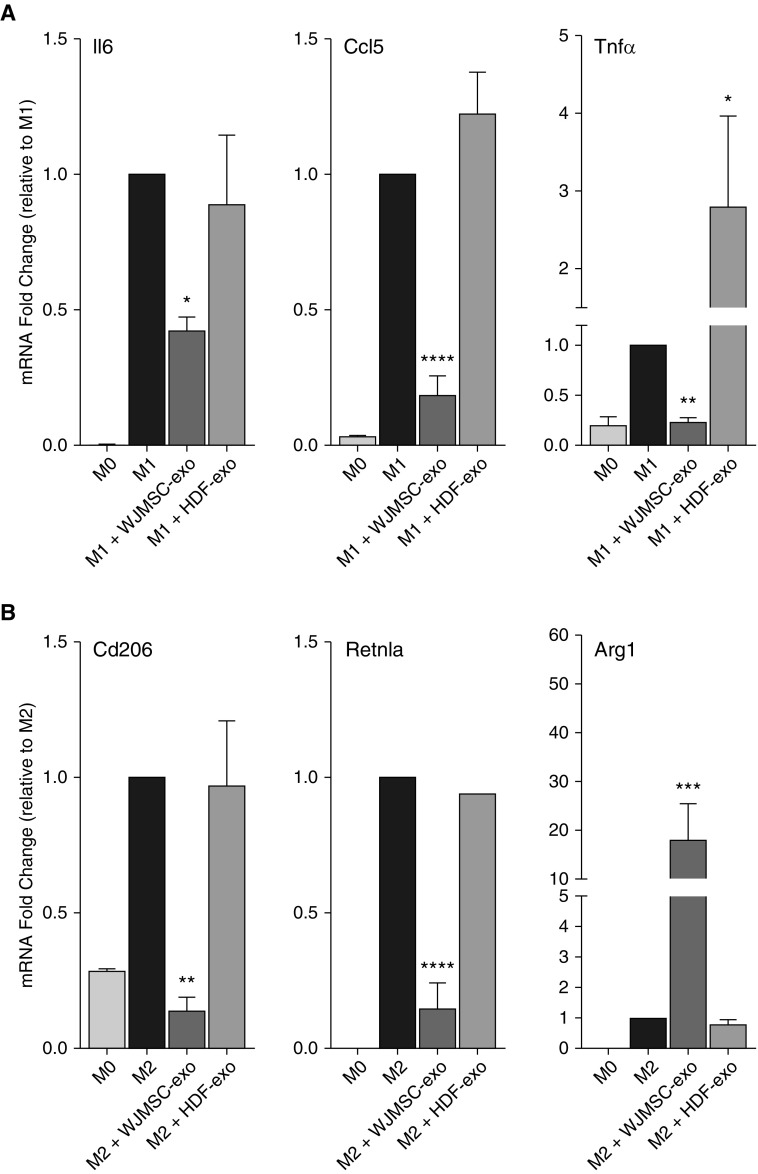
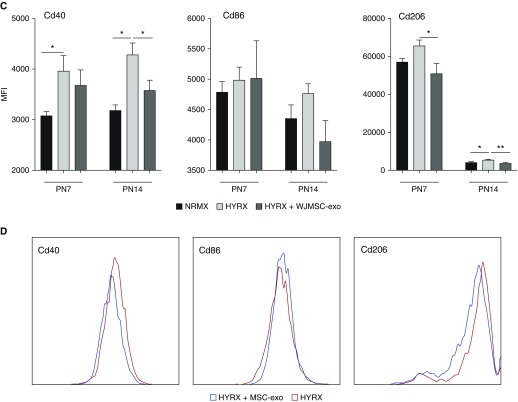
Figure 6.
Immunomodulatory capacity of Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem/stromal cell (WJMSC) exosomes (-exos): macrophage polarization potency assay. Macrophage polarization plays an important role in regulating the immune response and inflammation in the developing lung. The addition of WJMSC-exos to mouse bone marrow–derived macrophages or alveolar macrophages polarized to the proinflammatory M1 phenotype reduced the mRNA induction of markers, such as Il6, Ccl5, and Tnfα (A). The addition of WJMSC-exos to alternatively (M2) polarized macrophages super-induced arginase (Arg)-1 mRNA and modulated resistin-like alpha (Retnla) and Cd206 induction (B). Flow cytometry was used to assess lung macrophage (Cd45+ve, Cd11b−ve, Cd11c+ve, Cd64+ve) phenotype. M1 markers, Cd40 and Cd86, as well as M2 marker, Cd206, were assessed at Postnatal Day (PN) 7 and PN14. Median fluorescence intensity (MFI) was recorded (C). Representative histograms for Cd40, Cd86, and Cd206 (D). Data are shown as mean ± SEM; n = 4–8 per group. HDF = human dermal fibroblasts; HYRX = hyperoxia; NRMX = normoxia. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 versus M1 or M2 controls.