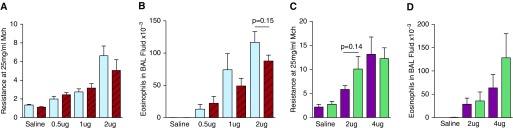
Figure 1.
Intratracheal inoculation with limiting doses of house dust mite extract (HDM) induces IgE- and FcεRIα-independent allergic airway disease (AAD). Wild-type (WT) and IgE-deficient FVB/N mice (A and B) and WT and FcεRIα-deficient BALB/c mice (C and D) were inoculated intratracheally with saline or HDM every other day for 14 days. Amounts of HDM shown denote protein delivered per inoculation. Resistance units are cm H2O × s/ml. (A and B) n = 5–15/group; three experiments pooled. Mice per each experimental group from left to right: 15, 14, 6, 5, 13, 13, 11, and 11. (C and D) n = 11–20/group; four experiments pooled. Mice per each experimental group from left to right: 20, 17, 15, 11, 12, and 13. FVB/N WT, blue bars; FVB/N IgE-KO, red bars; BALB/c WT, purple bars; BALB/c FcεRIα-KO, green bars. Data presented are means (±SEM). BAL, bronchoalveolar lavage; KO, knockout; Mch, methacholine.