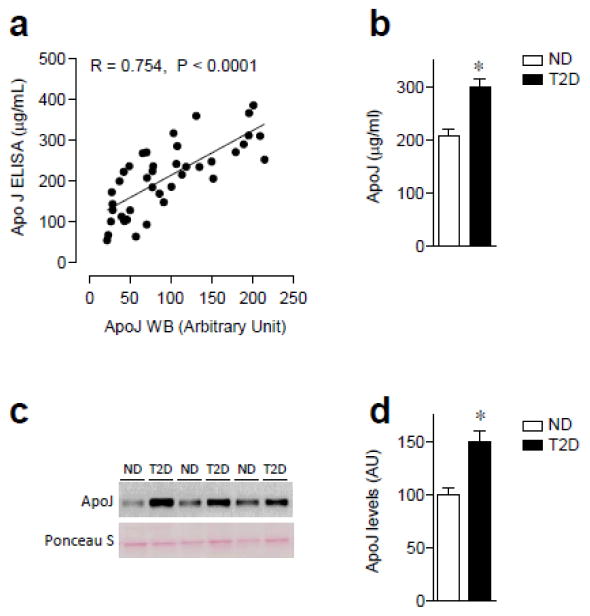
Figure 1. Serum levels of ApoJ in nondiabetic (ND) and type 2 diabetic (T2D) subjects.
(a) Correlation of ApoJ levels between western blotting analysis and ELISA in ND and T2D subjects. (b) Fasting serum ApoJ concentration in ND and T2D subjects. Serum ApoJ protein was measured by ELISA with 1:300 dilution of serum samples. Results are mean ± SEM for 13–27 subjects per group. *P<0.001 vs. ND. (c) Serum ApoJ protein in ND and T2D subjects. Proteins in sera were separated by SDS/PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. ApoJ proteins were visualized by immunoblotting in a non-reducing condition, which shows ~ 70 kDa as a single band. Ponceau S staining indicates that even amount of protein in each lane was loaded on the gel. Each lane in the blot represents a different subject. The immunoblots shown are representative of three blots. (d) Bars show densitometric quantitation of serum ApoJ from ND and T2D subjects. Results are means ± SEM for 26–27 subjects per group. *P<0.001 vs. ND.