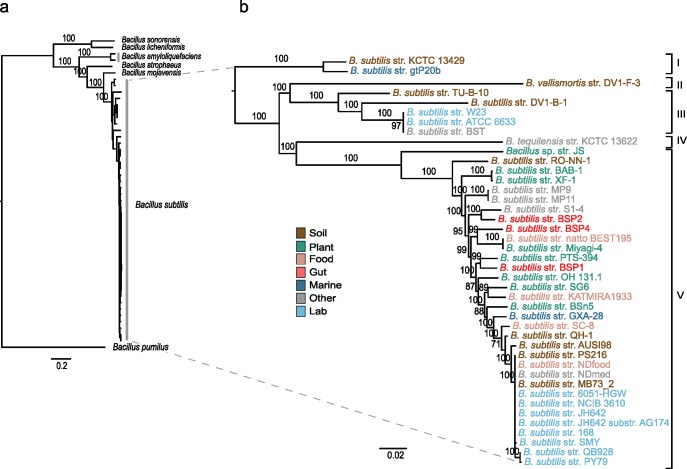
Fig. 1.
—The recent diversification of B. subtilis. (A) Phylogenetic analysis of B. subtilis strains and their closest relatives and (B) of the B. subtilis clade alone. ML (GTR + I+G + X) and bootstrap analyses were carried out on a concatenated data set of 685 core genes (520,227 nt). The tree was rooted following the results provided in supplementary figure S2, Supplementary Material online. Numbers on the nodes indicate bootstrap support, and the scale bar indicates the expected number of nucleotide substitutions per site. Due to the scale of the tree, some branches are too small for their statistical support to be shown; the cladogram in figure 3 distinguishes the branches with bootstrap support higher than 80%. The Roman numerals on the right indicate the five major branches of diversification within B. subtilis. The suggested taxonomic nomenclature for these branches is as follows: I B. subtilis inaquosorum, II B. subtilis vallismortis, III B. subtilis spizizenii, IV B. subtilis tequilensis, and V B. subtilis subtilis. Taxa are colored to indicate the niche at the site of sampling.