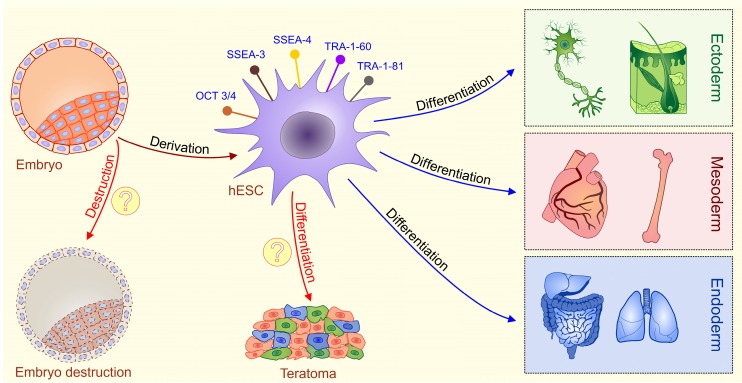
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram describing characteristics of ESCs. Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are harvested from a blastocyst. Embryonic stem (ES) cells are derived from the inner cell mass of the pre-implantation embryo. Fully characterized hESCs express typical pluripotent stem cell markers such as octamer-binding transcription factor 3/4 (OCT3/4), stage specific embryonic antigens 3 and 4 (SSEA-3 and SSEA-4), TRA-1-60, and TRA-1-81.These cells are pluripotent, meaning they can differentiate into cells from all three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm). Main ethical issues (labeled with question marks): isolation of ESCs involves the destruction of a human embryo; transplantation of undifferentiated ESCs may result with a formation of teratomas, tumors that contain all three germ layers.