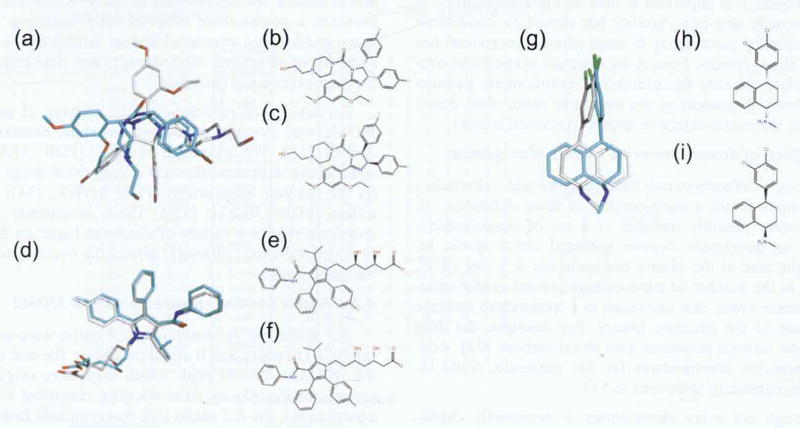
Fig. (3).
a) Comparison of the docking pose of the R,S Nutlin (from crystal structure; grey carbons) to the enantiomer (S,R; blue). When seeded into the NCI Diversity Set II for docking, the original form of nutlin (R,S) ranks 51 and the enantiomer ranks 3,482 (out of 3,718 docked structures). GScores are -6.70 kcal/mol (R,S) vs -3.95 (S,R). RMSD = 7.07. (b) Line structure of R,S Nutlin. (c) Line structure of S,R Nutlin. (d) Comparison of the docking pose of the R,R Atorvastatin (from crystal structure; grey carbons) to the enantiomer (R,R; blue). When seeded into the NCI Diversity Set II for docking, the S,S Atorvastatin ranks 1 and the enantiomer ranks 2 (out of 3,718 docked structures). GScores are -8.80 kcal/mol (S,S) vs -8.25 (R,R). RMSD = 0.70. (e) Line structure of R,R Atorvastatin. (f) Line structure of S,S Atorvastatin. (g) Comparison of the docking pose of the R,S Sertraline (from crystal structure; grey carbons) to the enantiomer (S,R: blue). Wlien seeded into the NCI Diversity Set II for docking, the R,S Sertraline ranks 67 and the enantiomer ranks 407 (out of 3,879 docked structures). GScores are -7.05 kcal/mol (R,S) vs -6.29 (S,R). RMSD = 2.64. (h) Line structure of R,S Sertraline, (i) Line structure of S, R Sertraline.