Optic neuropathies
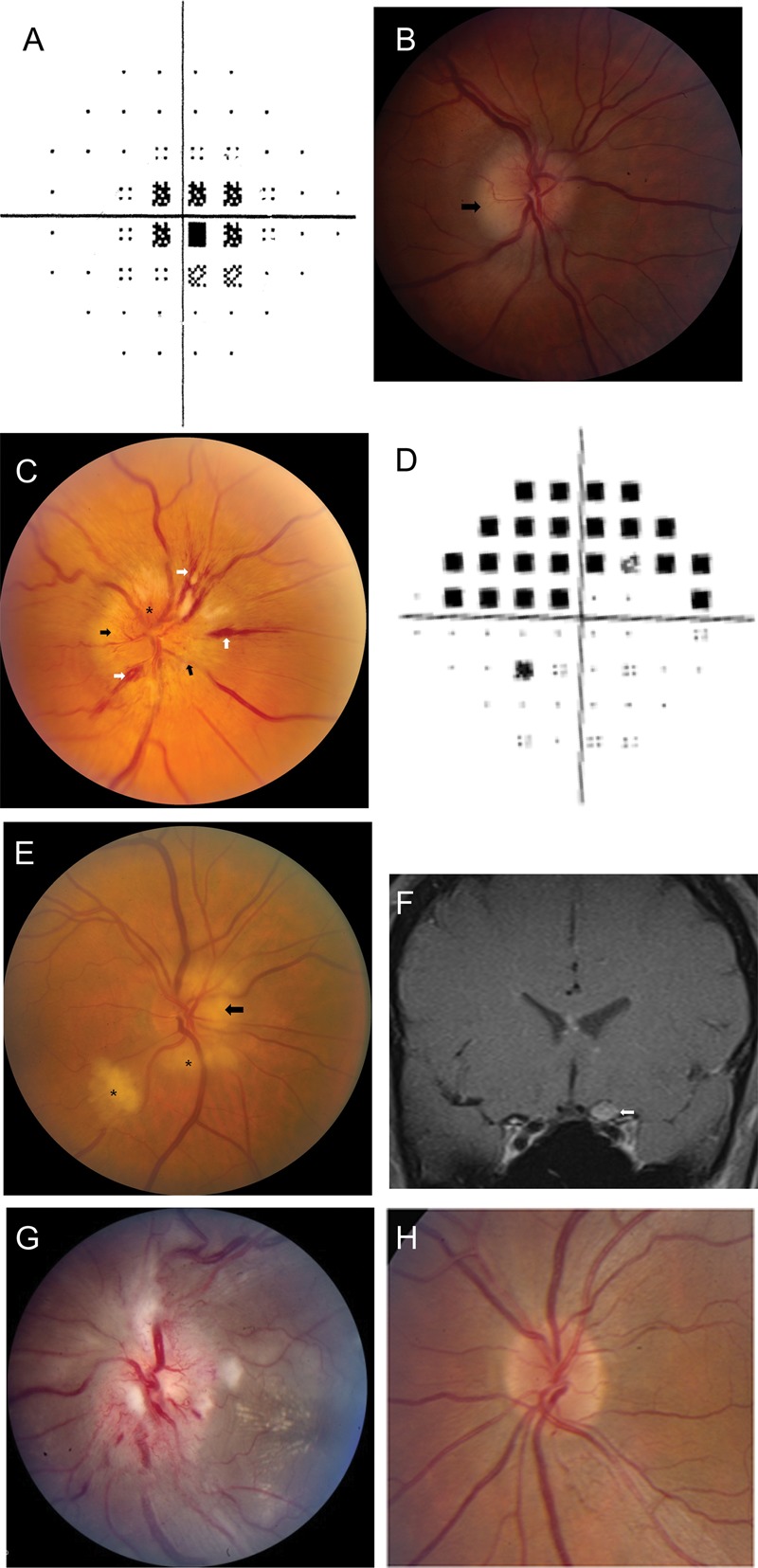
Figure 3. (A) Optic neuritis. Central scotoma on automated perimetry. (B) Optic neuritis. Mild optic disc edema, greatest in the temporal portion (arrow). (C) Nonarteritic ischemic optic neuropathy. Swelling of the optic nerve head (black arrows), splinter hemorrhages (white arrows), and hyperemia of the optic nerve head (asterisk). (D) Nonarteritic ischemic optic neuropathy. Superior arcuate altitudinal field deficit in the right eye. (E) Giant cell arteritis. Pallor and swelling of the optic nerve head (arrow), with retinal cotton wool spots (asterisks). (F) Neurosarcoidosis. Coronal postgadolinum MRI showing enlargement and pathologic enhancement of the left optic nerve (arrow). (G) Neuroretinitis. Marked disc swelling with hyperemia, surrounding cotton-wool spots, and macular exudate in a hemi-star pattern. (H) Leber hereditary optic neuropathy. Peripapillary telangiectasias (at 1 and 5 o'clock). B, C, E, and F reprinted with permission from Prasad et al.20
