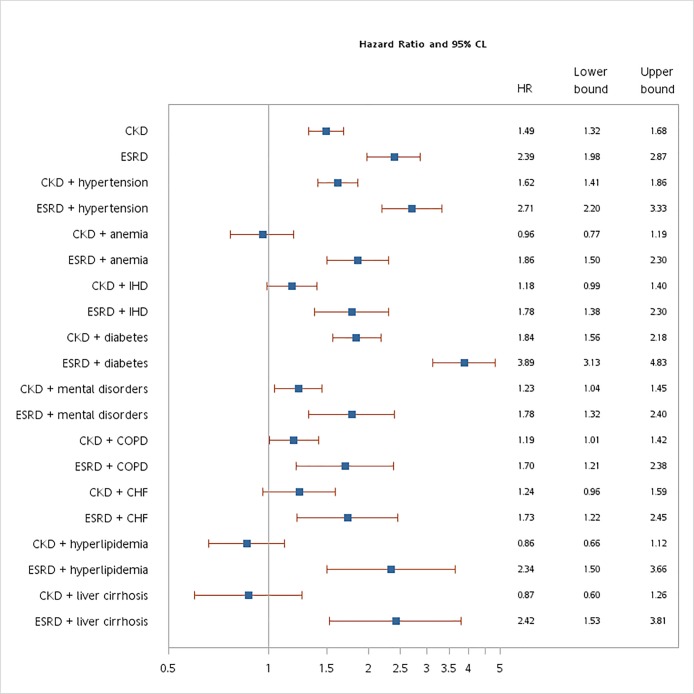
Fig 1. Incidence and risk of stroke for controls, CKD patients, and ESRD patients.
CI, confidence interval; CHF, heart failure; ESRD, end-stage renal disease; HR, hazard ratio; IHD, ischemic heart disease. Incidence showed per 1000 person-years. Compared with control group (n = 11024), all hazard rations adjusted for all covariates listed in Table 1 in 17 multivariate Cox proportional hazard models. Under the consideration of death as a competing risk, the hazard ratios of stroke for CKD patients and ESRD patients were 1.45 (95% CI 1.27–1.66) and 2.22 (95% CI 1.79–2.76), respectively. After matching with propensity score by all covariates listed in Table 1, the hazard ratios of stroke for CKD patients and ESRD patients were 1.51 (95% CI 1.24–1.85) and 2.08 (95% CI 1.32–3.26), respectively. The interaction terms of ESRD*sex (p<0.0001), ESRD*anemia (p<0.0001), ESRD*ischemic heart disease (p<0.0001), ESRD*diabetes (p<0.0001), ESRD*mental disorders (p = 0.0002), ESRD*chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (p = 0.0021), ESRD*heart failure (p = 0.0020), ESRD*hyperlipidemia (p = 0.0002), ESRD*liver cirrhosis (p = 0.0002) were added in the multivariate Cox proportional hazard models.