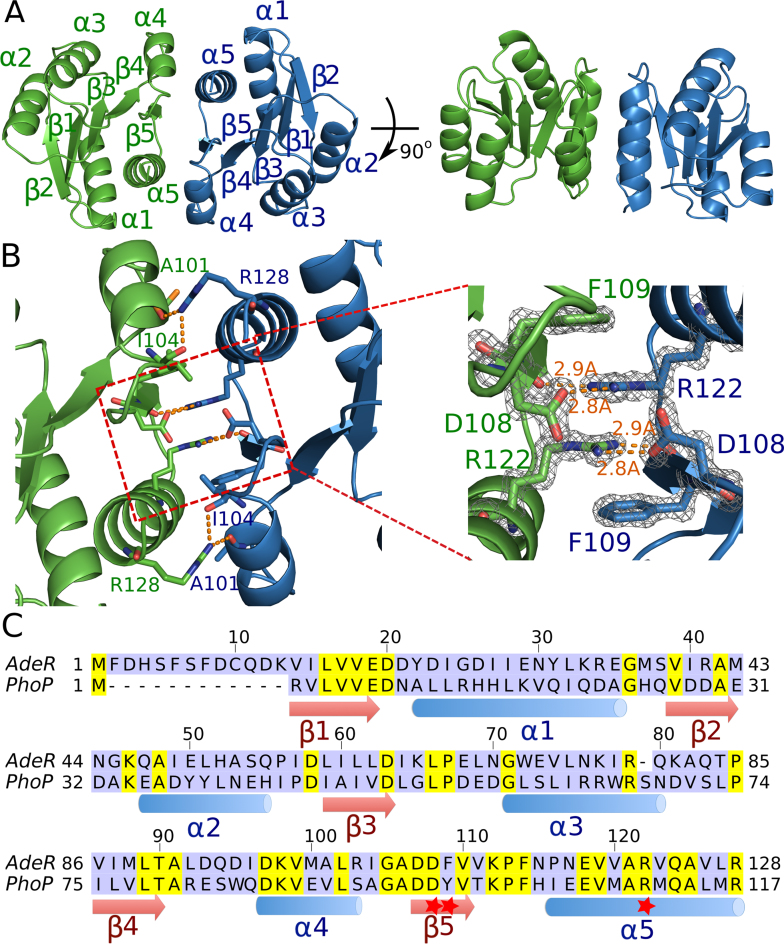
Figure 2.
Crystal structure of the AdeR receiver domain. (A) Crystal structure of the AdeR receiver domain dimer in different orientations. The AdeR receiver domain consist of five α helices and five β stands forming a parallel β in between, the α4–β5–α5 motif is involved in the dimerization. (B) Detailed interaction of residues involved in the AdeR receiver domain dimerization, the zoom-in view highlights D108, F109 and R122, forming a stable gear wheel like structure. The density map of D108, F109 and R122 are shown with 2Fo – Fc = 3σ. (C) Sequence alignment of AdeR and the response regulator PhoP receiver domain, secondary structures are denoted and the red star indicates the key residues involved in AdeR dimerization.