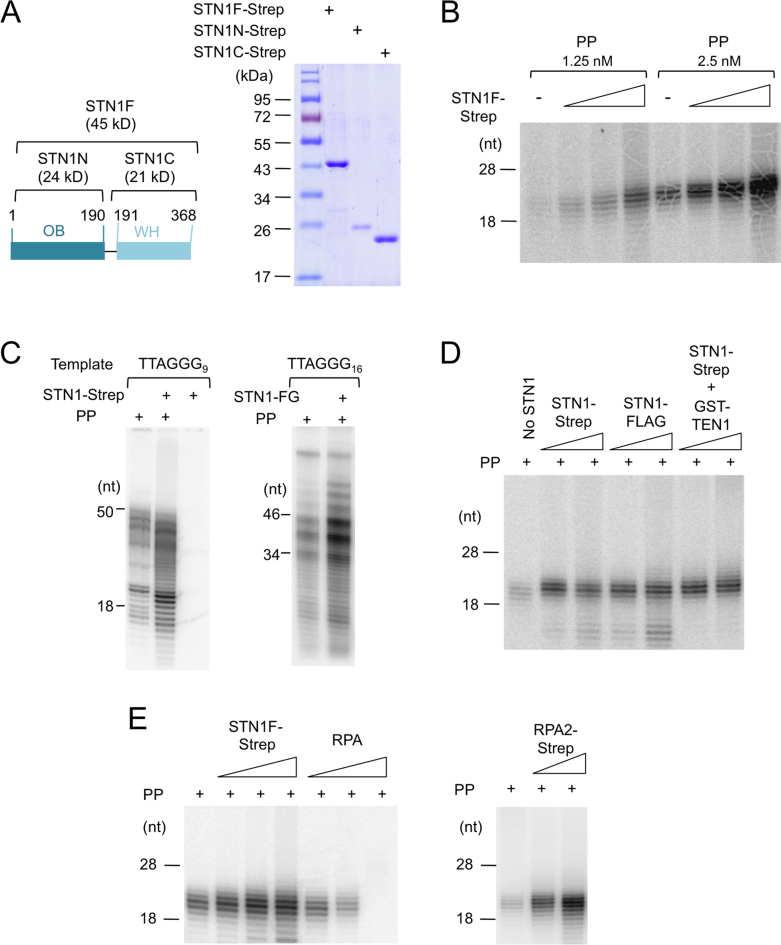
Figure 1.
Human STN1 stimulates the synthesis of RNA–DNA chimera by Primase-Pol α; the effects of STN1, STN1–TEN1 and RPA on PP activity (A) Human STN1s (FL, N and C) purified by two-step affinity chromatography (Ni-NTA and Strep-Tactin) were analyzed by 10% sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). (B) Human PP (1.25 and 2.5 nM) was tested in the coupled primase-polymerase assay using poly-dT as template in the presence of 0.17, 0.5 and 1.5 μM of full length STN1-Strep (STN1F-Strep). (C) Human PP (2.5 nM) was assayed for the synthesis of RNA–DNA chimera using the indicated G-strand templates in the absence or presence of Strep-tagged or FLAG-tagged STN1 (1 μM). (D) Human PP (1 nM) was assayed for the synthesis of RNA–DNA chimera using Poly-dT template in the presence of two different concentrations (0.5 and 1.5 μM) of STN1-Strep, STN1-FLAG or STN1-Strep/GST-TEN1 complex. (E) Human PP (2 nM) was assayed for the synthesis of RNA–DNA chimera using Poly-dT template in the presence of increasing concentrations of STN1-Strep (0.16, 0.5 and 1.5 μM) or RPA (0.053, 0.16 and 0.5 μM). In the right panel, 0.5 and 1.5 μM RPA2-Strep was added to the PP reaction.