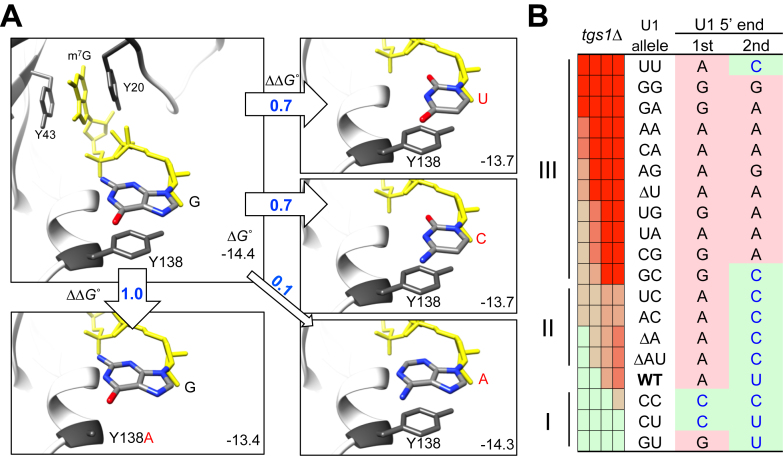
Figure 7.
In silico analysis of stacking between m7GpppG and Y138 residue in CBP20. (A) The G base immediately following the m7Gppp moiety (shown in yellow) was replaced by either U, C or A via molecular docking and the corresponding ΔGo values were computed (see Materials and Methods) and are shown at the lower right corner within each rectangular boxes. The resulting ΔΔGo values in reference to the wild-type state are indicated within or by the empty arrows. The previously experimentally tested Y138A mutation in relationship to m7GpppG is included as a control (box, lower left). (B) Striking correlation of the genetic data with the computationally predicted ΔΔGo (see text for detailed description). The precise 5′ ends of U1 transcripts (U1 5′ end) produced in all U1 snRNA mutants (i.e. U1 allele) are shown for their respective first (1st) and second (2nd) nucleotides in each row (see also Figure 2). Note that the (C/U)-(C/U), (G/A)-(C/U), and (G/A)-(G/A) combinations are predicted to cause weaker, wild-type-like, and excessive binding between U1 snRNA and CBP20, respectively. This pattern parallels to the Group I, II, and III assignments of the tgs1Δ synthetic lethality pattern (see also Figure 5).