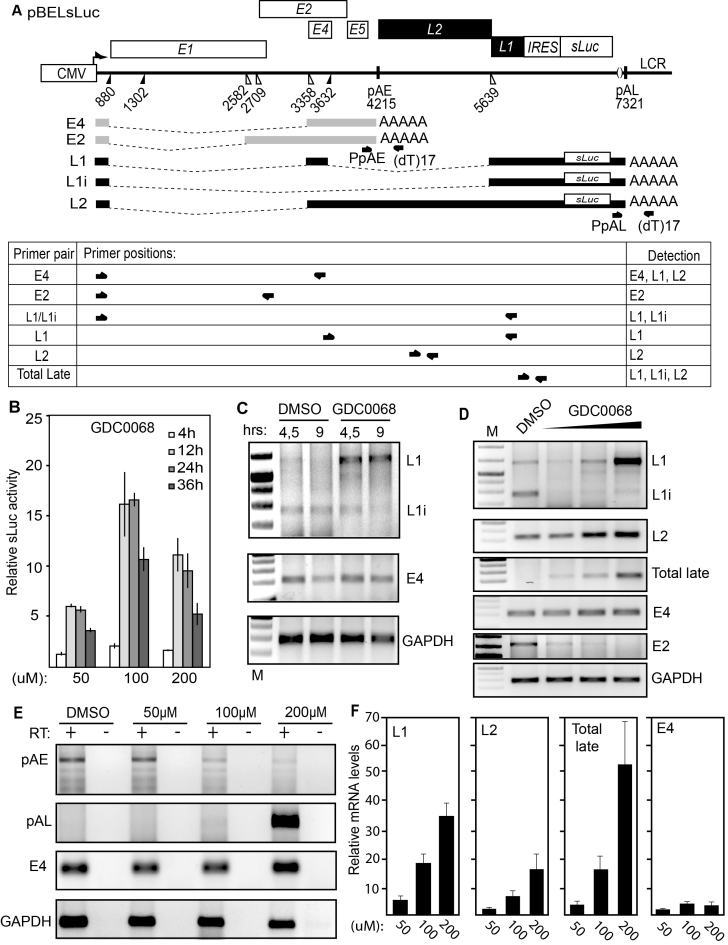
Figure 2.
(A) Schematic representation of the pBELsLuc reporter plasmid stably integrated in the genome of the C33A2 reporter cell line. Transcription of the HPV16 sequences in the pBELsLuc plasmid is driven by the human cytomegalovirus promoter (CMV). The sLuc gene inserted into the L1 region is indicated and is preceded by the poliovirus 2A internal ribosome entry site (IRES). HPV16 E2 and E4 mRNAs mRNAs produced by C33A2 cells are indicated in light grey (E2 and E4 mRNAs) and HPV16 late mRNAs encoding sLuc that can be induced in this reporter cell line are indicated in black. The location of RT-PCR primers is indicated below. (B) Secreted luciferase enzyme activity (sLuc) in the cell culture medium of reporter cell line C33A2 treated with various concentrations of the Akt kinase inhibitor GDC0068. sLuc activity was monitored at the indicated time points. sLuc activity is displayed as fold over DMSO-treated C33A2 cells at the various time points. (C) RT-PCR on total RNA extracted from the C33A2 reporter cell line treated with DMSO alone or Akti kinase inhibitor GDC0068 for 4.5hrs or 9hrs. The RT-PCR primers detected HPV16 L1/L1i-, E4- or GAPDH-mRNAs. (D) RT-PCR on total RNA extracted from the C33A2 reporter cell line treated with DMSO alone or various concentrations of Akt kinase inhibitor GDC0068 (50-, 100- or 200uM) for 9hrs. The RT-PCR primers detected HPV16 L1/L1i-, L2-, total late (L2 + L1 +L1i), E4-, E2- or GAPDH-mRNAs. (E) A 3′-RACE assay on total RNA extracted from C33A2 cells. Primers were F-Set2 and (dT)17-P3 for pAE and sLuc-S-inner and (dT)17-P3 for pAL (for primers see Supplementary Table S1). Spliced HPV16 E4 mRNAs and cellular GAPDH mRNAs are also shown. (F) RT-qPCR on the cDNA samples used for RT-PCR in Figure 2D.